Absorption, variable, and throughput costing EnRG Inc. produces trail mix packaged for sale in convenience stores in
Question:
Absorption, variable, and throughput costing EnRG Inc. produces trail mix packaged for sale in convenience stores in the Northeast section of the United States. At the beginning of April 2008, EnRG has no inventory of trail mix. Demand for the next three months is expected to remain constant at 50,000 bags per month. EnRG plans to produce to demand, 50,000 bags in April. However, many of the employees take vacation in June, so EnRG plans to produce 70,000 bags in May and only 30,000 bags in June.
Costs for the three months are expected to remain unchanged. The costs and revenues for April, May and June are expected to be:
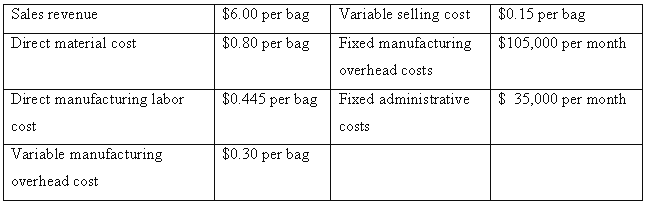
Suppose the actual costs, market demand, and levels of production for April, May, and June are as expected.
1. Compute operating income for April, May, and June under variable costing.
2. Compute operating income for April, May, and June under absorption costing. Assume that the denominator level for each month is that month’s expected level of output.
3. Compute operating income for April, May, and June under throughput costing.
4. Discuss the benefits and problems associated with using throughput costing.
Step by Step Answer:

Cost Accounting A Managerial Emphasis
ISBN: 978-0136126638
13th Edition
Authors: Charles T. Horngren, Srikant M.Dater, George Foster, Madhav





