The Edelman Gem Company, a small jewelry manufacturer, has been successful and has enjoyed a good growth
Question:
The Edelman Gem Company, a small jewelry manufacturer, has been successful and has enjoyed a good growth trend. Now Edelman is planning to go public with an issue of common stock, and it faces the problem of setting an appropriate price on the stock. The company and its investment bankers believe that the proper procedure is to select several similar firms with publicly traded common stock and to make relevant comparisons. Several jewelry manufacturers are reasonably similar to Edelman with respect to product mix, asset composition, and debt/equity proportions. Of these companies, Kennedy Jewelers and Strasburg Fashions are most similar. When analyzing the following data, assume that 1999 and 2004 were reasonably "normal" years for all three companies' that is, these years were neither especially good nor especially bad in terms of sales, earnings, and dividends. At the time of the analysis, rRF was 8 percent and RPM was 4 percent. Kennedy is listed on the AMEX and Strasburg on the NYSE, while Edelman will be traded in the NASDAQ market.
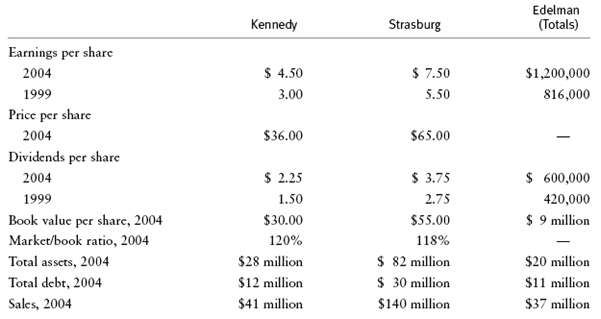
a. Assume that Edelman has 100 shares of stock outstanding. Use this information to calculate earnings per share (EPS), dividends per share (DPS), and book value per share for Edelman. (Hint: Edelman's 2004 EPS = $12,000.)
b. Calculate earnings and dividend growth rates for the three companies. (Hint: Edelman's EPS growth rate is 8 percent.)
c. On the basis of your answer to part a, do you think Edelman's stock would sell at a price in the same "ballpark" as that of Kennedy and Strasburg, that is, in the range of $25 to $100 per share?
d. Assuming that Edelman's management can split the stock so that the 100 shares could be changed to 1,000 shares, 100,000 shares, or any other number, would such an action make sense in this case? Why?
e. Now assume that Edelman did split its stock and has 400,000 shares. Calculate new values for EPS, DPS, and book value per share. (Hint: Edelman's new 2004 EPS is $3.00.)
f. Return on equity (ROE) can be measured as EPS/book value per share or as total earnings/total equity. Calculate ROEs for the three companies for 2004. (Hint: Edelman's 2004 ROE is 13.3 percent.)
g. Calculate dividend payout ratios for the three companies for both years. (Hint: Edelman's 2004 payout ratio is 50 percent.)
h. Calculate debt/total assets ratios for the three companies for 2004. (Hint: Edelman's 2004 debt ratio is 55 percent.)
i. Calculate the P/E ratios for Kennedy and Strasburg for 2004. Are these P/Es reasonable in view of relative growth, payout, and ROE data? If not, what other factors might explain them? (Hint: Kennedy's P/E = 8=.)
j. Now determine a range of values for Edelman's stock price, with 400,000 shares outstanding, by applying Kennedy's and Strasburg's P/E ratios, price/dividends ratios, and price/book value ratios to your data for Edelman. For example, one possible price for Edelman's stock is (P/E Kennedy) (EPS Edelman) = 8($3) = $24 per share. Similar calculations would produce a range of prices based on both Kennedy's and Strasburg's data. (Hint: Our range was $24 to $27.)
k. Using the equation rs = D1/P0 = g, find approximate rs values for Kennedy and Strasburg. Then use these values in the constant growth stock price model to find a price for Edelman's stock. (Hint: We averaged the EPS and DPS g's for Edelman.)
l. At what price do you think Edelman's shares should be offered to the public? You will want to select a price that will be low enough to induce investors to buy the stock but not so low that it will rise sharply immediately after it is issued. Think about relative growth rates, ROEs, dividend yields, and total returns (rs = D1/P0 + g).
Common StockCommon stock is an equity component that represents the worth of stock owned by the shareholders of the company. The common stock represents the par value of the shares outstanding at a balance sheet date. Public companies can trade their stocks on... Dividend
A dividend is a distribution of a portion of company’s earnings, decided and managed by the company’s board of directors, and paid to the shareholders. Dividends are given on the shares. It is a token reward paid to the shareholders for their...
Step by Step Answer:

Financial management theory and practice
ISBN: 978-0324422696
12th Edition
Authors: Eugene F. Brigham and Michael C. Ehrhardt





