David Johnson has decided that a company is the best business structure for him and on 15
Question:
David Johnson has decided that a company is the best business structure for him and on 15 July Electronic Thingz Pty Ltd was incorporated as a private company with David as the sole director/shareholder. The company now has a tax file number and an Australian Business Number (Australian students), an IRD number (New Zealand students), and David has chosen not to register the company for GST at present.
David has signed a lease on a shop for 2 years with an option to renew for a further 3 years. He has opened a bank account in the company’s name with the ANZ Bank, and at the same time applied for a loan of $50,000 from the bank to enable him to set up the shop and provide him with working capital. He contracted a shopfitter to fit out the shop, which opened for business on 24 July.
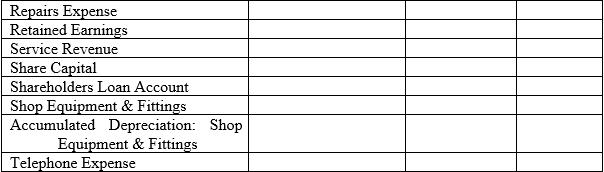
As David’s accountant you have recommended that the following accounts be used as a guide when setting up the chart of accounts for the general ledger: Accountancy Fees (600), Accounts Payable (200), Accounts Receivable, Advertising Expense, Bank Fees, Bank Loan, Borrowing Expense, Cash at Bank (100), Depreciation Expense, Discount Allowed, Dividends, Electricity Expense, Insurance Expense, Interest Expense, Motor Vehicles Expense, Motor Vehicles (160), Accumulated Depreciation: Motor Vehicles (161), Office Supplies Expense, Prepaid Advertising (130), Prepaid Insurance, Prepaid Rent, Rent Expense, Repairs Expense, Retained Earnings, Service Revenue (400), Share Capital (300), Shareholders Loan Account, Shop Equipment & Fittings, Accumulated Depreciation: Shop Equipment & Fittings, Telephone Expense.
These are the transactions for the month.
Required
(a) Analysing/decision making Use the worksheet provided below to create the chart of accounts ensuring that you correctly classify the accounts by type i.e. asset, liability, equity, revenue, cost of sales, and expenses. A few account numbers have been provided as a guide. Asset accounts begin with the number 1, liabilities with 2, equity with 3, income with 4, cost of sales with 5, and expenses with 6.
The currenton-current column is for the asset and liability accounts in the Statement of Financial Position. Recall: current assets are cash and other assets that are reasonably expected to be converted to cash or used in the business within 1 year or the operating cycle, whichever is longer, and non-current assets are assets that are not expected to be consumed or sold within 1 year or the operating cycle and have not been purchased for trading purposes. Current liabilities are obligations reasonably expected to be paid within the next year or operating cycle, whichever is the longer, and non-current liabilities are liabilities that are not expected to be paid within 1 year or the operating cycle. 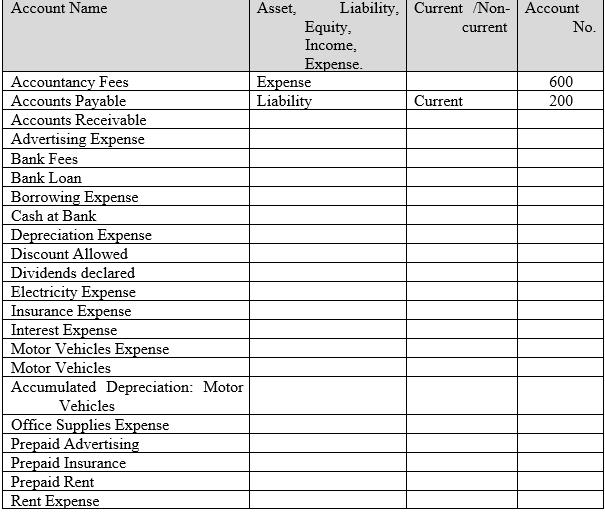
(b) Recording Use the general journal to record the transactions for July, with narrations.
(c) Recording Setup the general ledger T accounts and post the journal entries to them. Remember to include posting references as they provide an audit trail. Use pencil to subtotal and calculate the balance of each account. Do not close off these accounts as they will be used again in the next chapter.
(d) Reporting Prepare a trial balance on 31 July.
Step by Step Answer:

Accounting
ISBN: 9780730382737
11th Edition
Authors: John Hoggett, John Medlin, Keryn Chalmers, Claire Beattie





