Suppose you were investigating the correlation between intermolecular forces and the way in which molecules cohere to
Question:
Suppose you were investigating the correlation between intermolecular forces and the way in which molecules cohere to each other in a liquid and decided that you can gain some insight by comparing the entropies of vaporization of several liquids.
Calculate the entropy of vaporization of acetone at 296 K with an external pressure of 1 bar. The molar heat capacity of liquid acetone is 127 J · K–1 · mol–1, its boiling point is 329.4 K, and its enthalpy of vaporization is 29.1 kJ · mol–1.
PLAN
Step 1 Use Eq. 4 to calculate the entropy change accompanying the heating of acetone from the “initial” temperature of 296 K to the “final” temperature of 329.4 K. The heat capacity of liquid acetone is approximately constant over this range.
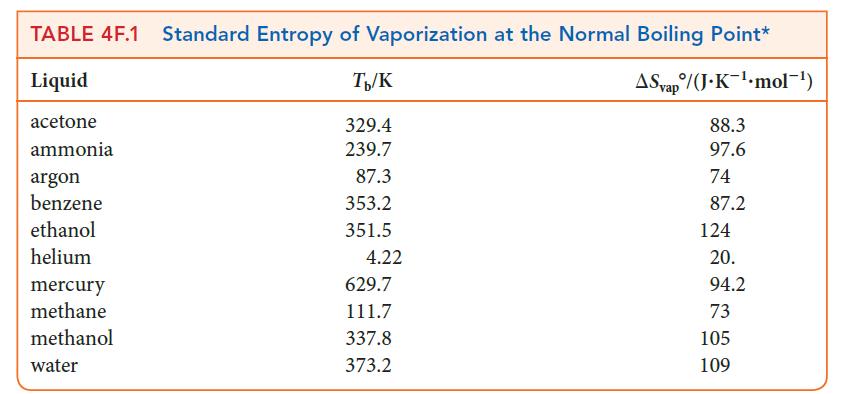
Step 2 Use Eq. 5 to calculate the entropy of vaporization or look up the value in Table 4F.1.
Step 3 Use Eq. 4 to calculate the entropy change accompanying the cooling of acetone vapor from the new “initial” temperature of 329.4 K back to the new “final” temperature of 296 K (a negative value). The heat capacity of acetone vapor may be estimated from the equipartition theorem (Topic 4B) as CP,m = 4R.
Step 4 Sum the three entropy changes to give DSvap°(296 K).
What should you assume? Assume that acetone vapor is an ideal gas and that only translations and rotations contribute to the gas-phase heat capacity.
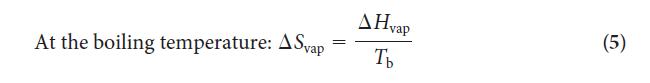
Step by Step Answer:

Chemical Principles The Quest For Insight
ISBN: 9781464183959
7th Edition
Authors: Peter Atkins, Loretta Jones, Leroy Laverman





