Muscle cells need energy to contract. One biochemical pathway for energy transfer is the breakdown of glucose
Question:
Muscle cells need energy to contract. One biochemical pathway for energy transfer is the breakdown of glucose to pyruvate in a process called glycolysis. In the presence of sufficient oxygen in the cell, pyruvate is oxidized to CO2 and H2O to make further energy available. However, under extreme conditions not enough oxygen can be supplied to the cells, so muscle cells produce lactate ion according to the reaction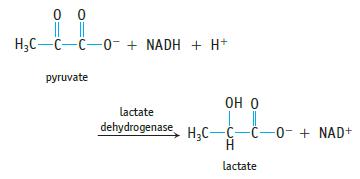
where ΔrG°′ = −25.1 kJ/mol. In living cells, the pH value is about 7. The hydronium ion concentration is constant and is included in ΔG°, which is then called ΔrG°′ (Applying Chemical Principles 18.1 Thermodynamics and Living Things). (This problem is taken from the problems for the 36th International Chemistry Olympiad for high school students held in Kiel, Germany, in 2004.)
(a) Calculate ΔrG° for the reaction at 25°C.
(b) Calculate the equilibrium constant K′. (The hydronium ion concentration is included in the constant. That is, K′ = K ∙ [H3O+] for the reaction at 25°C and pH = 7.0.)
(c) ΔrG°′ is the free energy change under standard conditions; that is, the concentrations of all reactants (except H3O+) are 1.00 mol/L. Calculate ΔrG′ at 25°C, assuming the following concentrations in the cell: pyruvate, 380 μmol/L; NADH, 50 μmol/L; lactate ion, 3700 μmol/L; and NAD+ ion, 540 μmol/L.
Step by Step Answer:

Chemistry And Chemical Reactivity
ISBN: 9780357001172
10th Edition
Authors: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel





