Suppose a cosmic ray colliding with a nucleus in the Earth's upper atmosphere produces a muon that
Question:
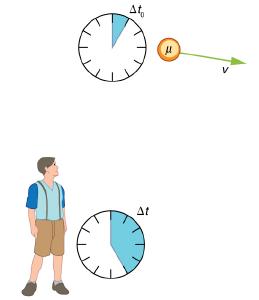
Suppose a cosmic ray colliding with a nucleus in the Earth's upper atmosphere produces a muon that has a velocity v = 0.950c. The muon then travels at constant velocity and lives 1.52 μs as measured in the muon's frame of reference. (You can imagine this as the muon's internal clock.) How long does the muon live as measured by an Earth-bound observer? (See Figure 28.7.)
Strategy
A clock moving with the system being measured observes the proper time, so the time we are given is Δt0 = 1.52 μs. The Earth-bound observer measures At as given by the equation Δt=yΔt0. Since we know the velocity, the calculation is straightforward.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





