The following three problems in this Exercise refer to a function f that calls another function func.
Question:
The following three problems in this Exercise refer to a function f that calls another function func. The code for C function func is already compiled in another module using the MIPS calling convention from Figure 2.14. The function declaration for func is “int func(int a, int b);”. The code for function f is as follows:
Figure 2.14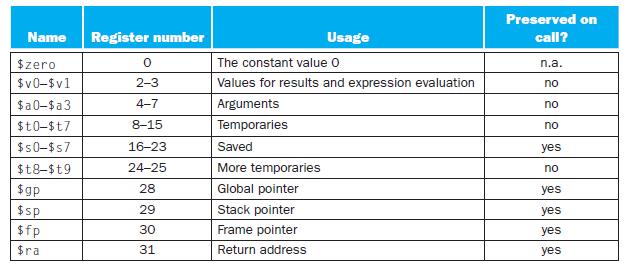

Right before your function f from Problem 2.19.4 returns, what do we know about contents of registers $t5, $s3, $ra, and $sp? Keep in mind that we know what the entire function f looks like, but for function func we only know its declaration.
Data from problem 2.19.4
Translate function f into MIPS assembly language, also using the MIPS calling convention from Figure 2.14. If you need to use registers $t0 through $t7, use the lower-numbered registers first.
Step by Step Answer:

Computer Organization And Design The Hardware Software Interface
ISBN: 9780123747501
4th Revised Edition
Authors: David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy





