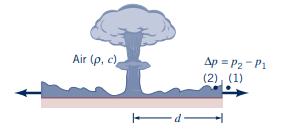
The pressure rise, (Delta p), across a blast wave, as shown in Fig. P7.61, is assumed to
Question:
The pressure rise, \(\Delta p\), across a blast wave, as shown in Fig. P7.61, is assumed to be a function of the amount of energy released in the explosion, \(E\), the air density, \(ho\), the speed of sound, \(c\), and the distance from the blast, \(d\).
(a) Put this relationship in dimensionless form.
(b) Consider two blasts: the prototype blast with energy release \(E\) and a model blast with \(1 / 1000\) th the energy release \(\left(E_{m}=0.001 E\right)\). At what distance from the model blast will the pressure rise be the same as that at a distance of 1 mile from the prototype blast?
Figure P7.61
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Munson Young And Okiishi's Fundamentals Of Fluid Mechanics
ISBN: 9781119080701
8th Edition
Authors: Philip M. Gerhart, Andrew L. Gerhart, John I. Hochstein
Question Posted:





