Founded in 1984 by S. Narayanan and H. Nandi, MRO-TEK started with the initial focus on network
Question:
Founded in 1984 by S. Narayanan and H. Nandi, MRO-TEK started with the initial focus on network computing with indigenously developed Line Drivers and Modems. The company became a leader in the networking and last mile access segment.
In a span of 24 years, MRO-TEK has evolved and grown from revenue of a mere ₹2 lakhs to ₹1.3 billion. Lately, the firm has been hurt due to the aggressive growth of the wireless technologies. This has led to a negative growth and erratic performance in the company for the last few years.
We probe into FY2005-06 numbers of the firm’s inventories, receivables, and investments. From the FY2006 Annual Report of MRO-TEK Limited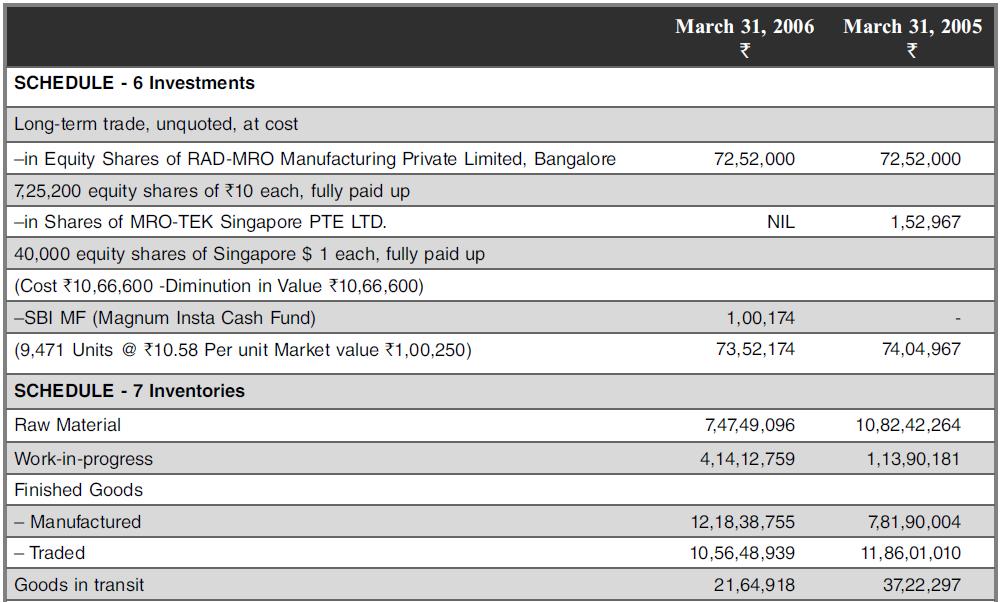


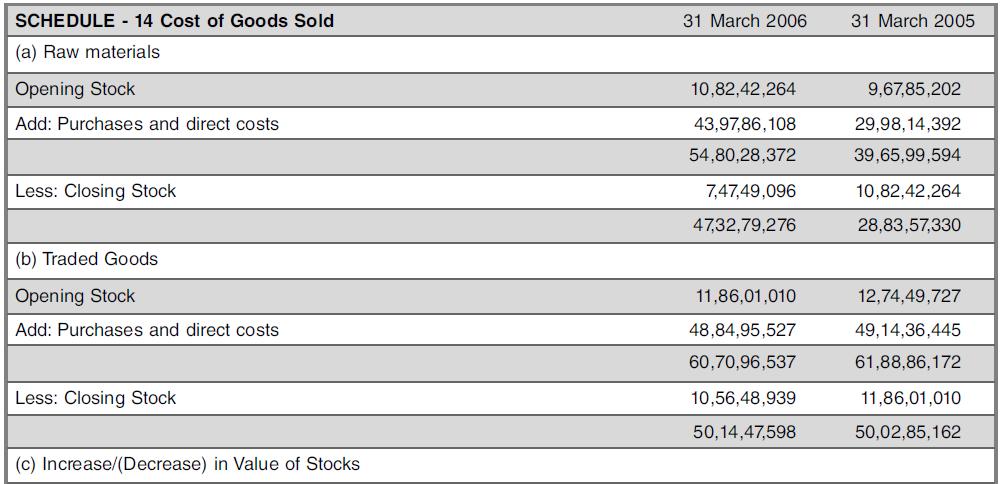
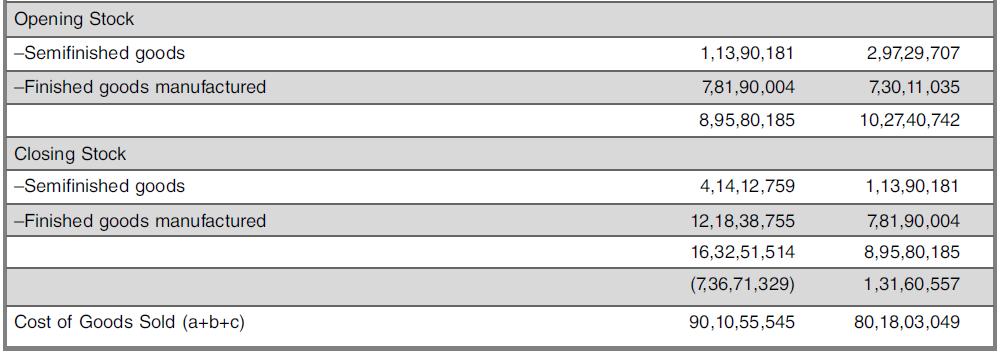
The company’s notes to above schedules included the following text:
Inventories:
(a) Raw Materials, Finished (Traded) Goods & Goods in Transit are valued at lower of cost and netrealizable value, on First-In, First-Out basis.
(b) Semi-Finished Goods and Finished (manufactured) Goods, are valued at lower of cost (including an appropriate portion of overheads up to the respective stage/s of completion) and, net realizable value, on First-In, First-Out basis. Raw-materials includes a sum of ₹NIL (₹42,498), being the value of material with Sub-Contractors.
Finished Goods includes
(a) ₹10,05,506 (₹37,98,774), being value of material for demonstration purposes at prospective customers’ premises.
(b) ₹38,646 (₹28,78,738), being value of material for rectification purposes, at suppliers’ premises.
Investments:
Investments are classified as current investments and long-term investments. Long-term investments are stated at cost (except where there is a diminution in value other than temporary, in which case, the carrying value is reduced to recognize the decline). Current investments are stated at lower of cost or fair market value.
Diminution in Value of Investments:
During the year, the company has provided for diminution in the value of Long-term Investments in Share Capital of MRO-TEK (Singapore) Pte. Ltd., Singapore, the Joint Venture Company, to the extent of ₹1,53,967 (₹NIL), being the decline in the value of investments, other than temporary decline, Consequent upon filing of an application filed with the respective authorities, for voluntary winding up of the said Company.
Sundry Debtors
Sundry Debtors reflected under schedule 8 is net of ₹68,24,500, being value of Letters of Credit received from the company’s customers discounted with the Bank.
Case question
(a) What are the new terms you come across in the above excerpts of MRO-TEKs annual report?
(b) What are the significant changes in the long-term investments of the company? Can you write accounting records for the above changes? Are the changes good or bad? Discuss.
(c) What are the significant changes in the accounts receivable of the company? What do the terms “Inward LC Discount” and “Provision for Bad and Doubtful Debts” mean? Comment on their impact? Should a company have more of such items? Discuss
(d) As part of its inventories and cost of goods sold, why is the company having three opening stocks and closing stocks? What is the significance of these items? Inside the company what would be the process of finalizing the inventory and cost of goods sold details of the company?
Step by Step Answer:

Financial Accounting For Management
ISBN: 9789385965661
4th Edition
Authors: Neelakantan Ramachandran, Ram Kumar Kakani





