(a) Suppose a projectile is launched vertically from the surface r = R of the earth with...
Question:
(a) Suppose a projectile is launched vertically from the surface r = R of the earth with initial velocity v0 = √2GM/R, so v20 = k2/R where k2 = 2GM. Solve the differential equation dr/dt = k/√r (from Eq. (23) in this section) explicitly to deduce that r(t) → ∞ as t → ∞.
(b) If the projectile is launched vertically with initial velocity v0 > √2GM/R, deduce that
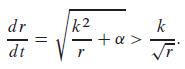
Why does it again follow that r(t) → ∞ as t → ∞?
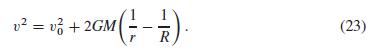
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Differential Equations And Linear Algebra
ISBN: 9780134497181
4th Edition
Authors: C. Edwards, David Penney, David Calvis
Question Posted:





