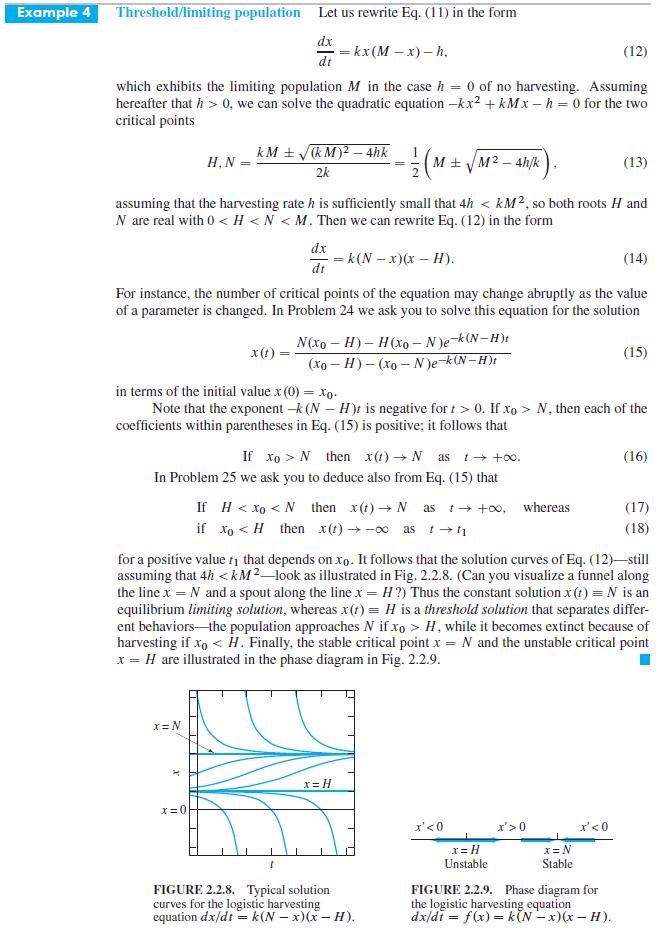
Example 4 dealt with the case 4h > kM 2 in the equation dx/dt = kx (M
Question:
Example 4 dealt with the case 4h > kM2 in the equation dx/dt = kx (M - x) - h that describes constant-rate harvesting of a logistic population. Problems 26 and 27 deal with the other cases.
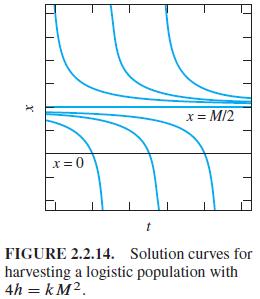
If 4h = kM2, show that typical solution curves look as illustrated in Fig. 2.2.14. Thus if x0 ≧ M/2, then x (t) → M/2 as t →+ ∞. But if x0 < M/2, then x (t) = 0 after a finite period of time, so the lake is fished out. The critical point x = M/2 might be called semistable, because it looks stable from one side, unstable from the other.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Differential Equations And Linear Algebra
ISBN: 9780134497181
4th Edition
Authors: C. Edwards, David Penney, David Calvis
Question Posted:





