Oil of viscosity (mu=0.0357 mathrm{~Pa} cdot mathrm{s}) and density (ho=) (0.796 mathrm{~kg} / mathrm{m}^{3}) is sandwiched in
Question:
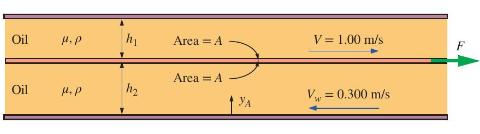
Oil of viscosity \(\mu=0.0357 \mathrm{~Pa} \cdot \mathrm{s}\) and density \(ho=\) \(0.796 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}\) is sandwiched in the small gap between two very large parallel flat plates. A third flat plate of surface area \(A=20.0 \mathrm{~cm} \times 20.0 \mathrm{~cm}\) (on one side) is dragged through the oil at steady velocity \(V=1.00 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\) to the right as sketched.
The top plate is stationary, but the bottom plate is moving at velocity \(V=0.300 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\) to the left as sketched. The heights are \(h_{1}=1.00 \mathrm{~mm}\) and \(h_{2}=1.65 \mathrm{~mm}\). The force required to pull the plate through the oil is \(F\).
(a) Sketch the velocity profiles and calculate the distance \(y_{A}\) where the velocity is zero. Since the gaps are small and the oil is very viscous, the velocity profiles are linear in both gaps. Use the no-slip conditions at the walls to determine the velocity profile in each gap.
(b) Calculate force \(F\) in newtons (N) required to keep the middle plate moving at constant speed.
Step by Step Answer:

Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
ISBN: 9781259696534
4th Edition
Authors: Yunus Cengel, John Cimbala




