In a manufacturing process, an organic solvent (methyl ethyl ketone, MEK) is used to dissolve a thin
Question:
a. What are the Schmidt number and the average Sherwood number for the mass-transfer process?
b. What is the average flux of dissolved polymer (in units of g A/cm2 · s) from the surface?
c. Plot out the local kc,x vs. position x, for 0 < x ‰¤ L.
d. Eventually, the polymer film will completely dissolve away from the entire surface. However, before this time the thickness of the polymer film remaining on the flat surface will not be uniform. Plot out what a plot of polymer film thickness (e) vs. position x would look like at three different times before the polymer film is completely dissolved.
e. What are the hydrodynamic (δ) and concentration boundary- layer (δc) thicknesses at x = 10 cm?
Potentially useful data: DAB = 3.0 × 10-6 cm2/s, the diffusion coefficient of dissolved polymer (solute A) in liquid MEK solvent at 25°C; ÏA,solid = 1.05 g/cm3, mass density of solid polymer film material; cAs = cA = 0.04 g/cm3, maximum solubility of dissolved polymer (solute A) in MEK solvent at 25°C; vB = 6.0 × 10-3 cm2/s, kinematic viscosity of liquid MEK at 25°C; ÏB = 0.80 g/cm3, mass density of liquid MEK solvent at 25°C. 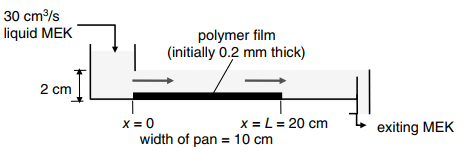
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Momentum Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781118947463
6th Edition
Authors: James Welty, Gregory L. Rorrer, David G. Foster





