Wastewater containing solute A at concentration of 1.0 · 10 gmole/m 3 enters an open tank at
Question:
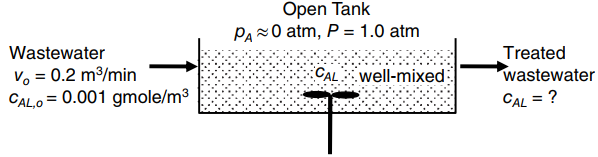
a. Determine the % resistance to mass-transfer in the liquid film.
b. Determine the bulk concentration cAL in the exiting liquid stream, and cAL,i the concentration of solute A at the liquid interface.
c. In the above system, the flux NA would increase by increasing which of the following: the liquid volume level in the tank at fixed surface area; the agitation intensity of the bulk liquid; the agitation intensity of the bulk gas; the inlet liquid volumetric flow rate; the system temperature.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Fundamentals Of Momentum Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781118947463
6th Edition
Authors: James Welty, Gregory L. Rorrer, David G. Foster
Question Posted:





