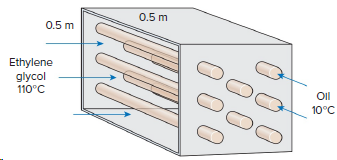
Consider a cross-flow engine oil heater that uses ethylene glycol flowing at a temperature of 110°C to
Question:
(a) Mass flow rate of ethylene glycol
(b) Number of tube rows. In your calculation use the following properties for the ethylene glycol.
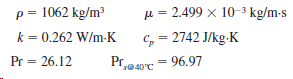
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Fundamentals of Thermal-Fluid Sciences
ISBN: 978-0078027680
5th edition
Authors: Yunus A. Cengel, Robert H. Turner, John M. Cimbala
Question Posted:





