Annular packed beds (APBs) involving the flow of fluids are used in many technical and engineering applications,
Question:
Annular packed beds (APBs) involving the flow of fluids are used in many technical and engineering applications, such as in chemical reactors, heat exchangers, and fusion reactor blankets. It is well known that the wall in a packed bed affects the radial void fraction distribution. Since APBs have two walls that can simultaneously affect the radial void fraction distribution, it is essential to include this variation in transport models. A correlation for this purpose was recently formulated (Mueller, 1999). The correlation is restricted to randomly packed beds in annular cylindrical containers of outside diameter $D_{o}$, inside diameter $D_{i}$, equivalent diameter $D_{e}=D_{o}-D_{i}$, consisting of equal-sized spheres of diameter $d_{p}$, with diameter aspect ratios of $4 \leq D_{e} / d_{p} \leq 20$. The correlation is
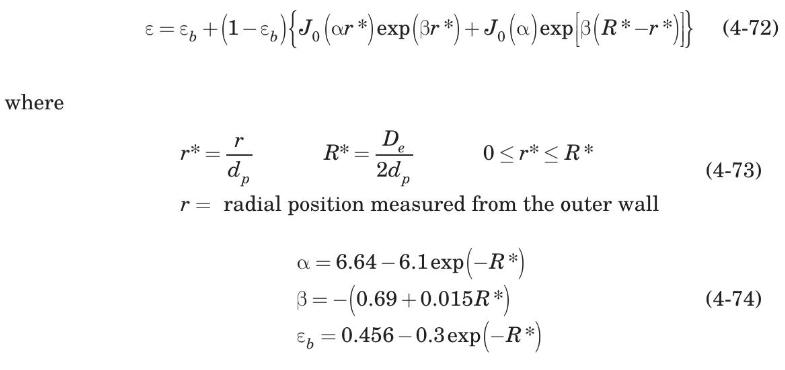
Consider an APB with outside diameter of $140 \mathrm{~mm}$, inside diameter of $40 \mathrm{~mm}$, packed with identical $10-\mathrm{mm}$-diameter spheres.
(a) Estimate the void fraction at a distance from the outer wall of $25 \mathrm{~mm}$.
(b) Plot the void fraction, as predicted by equation (4-72), for $r^{*}$ from 0 to $R^{*}$.
(c) Show that the average porosity for an APB is given by
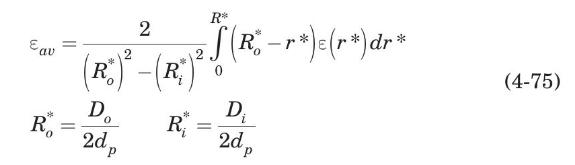
(d) Estimate the average porosity for the APB described above.
Step by Step Answer:





