Suppose that a laboratory experiment requires that an aqueous solution be delivered to an open container at
Question:
Suppose that a laboratory experiment requires that an aqueous solution be delivered to an open container at a constant flow rate of 100 μl/min for 30 min. A syringe pump is available, which has a motor and gear drive that will advance the plunger of any syringe at a set speed. As shown in Fig. P2.4, the syringe diameter is Ds and the pusher speed is Us. The syringe will be connected to plastic tubing with a length L = 50 cm and a diameter D = 0.86 mm. There may be a height difference between the ends of the tubing. A syringe size must be chosen.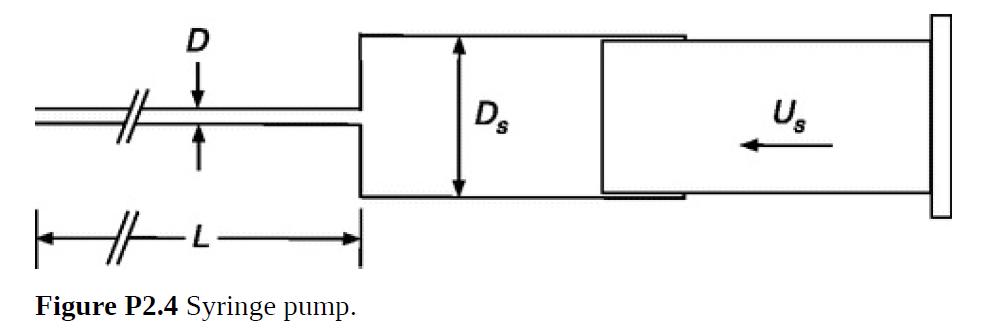
(a) According to the pump manufacturer, Us can be controlled from 0.08 to 80 mm/min. Three syringe sizes available in the particular lab are 1 ml (Ds = 4.8 mm), 5 ml (Ds = 12.1 mm), and 50 ml (Ds = 26.7 mm). Which would be best?
(b) If the tubing inlet and outlet are at the same height, what will |ΔP| be within the tubing? Will it be affected by the size of the syringe?
(c) If the tubing outlet is raised by 10 cm, what will the new |ΔP| be?
Step by Step Answer:

Introduction To Chemical Engineering Fluid Mechanics
ISBN: 9781107123779
1st Edition
Authors: William M. Deen





