Founded in 1960, the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is an intergovernmental organization of 14 nations
Question:
Founded in 1960, the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is an intergovernmental organization of 14 nations that meets periodically in order to establish oil production quotas for each individual nation, resulting in greater profits overall. However, OPEC has a history of failing to enforce its own quota limits. Consider a simplified example with just two countries: Venezuela and Kuwait. Currently, both countries are producing 2.5 million barrels per day. If both countries agree to cooperate with each other, they will each restrict output to 2 million barrels per day, causing the price of oil to rise. If one of the countries defects from the agreement, they will produce 2.5 million barrels and total output will rise from 4 million barrels to 4.5 million barrels. As a result, the price will fall slightly. If both nations defect from the agreement, each nation will again produce 2.5 million barrels and the price will fall to the original level. The payoffs for each possible outcome are illustrated in the following payoff table:
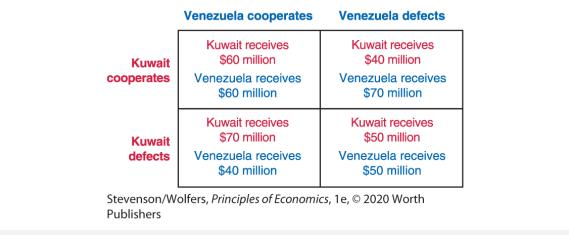
a. In terms of their collective profits, what is the best outcome for Kuwait and Venezuela?
b. What is the Nash equilibrium outcome? Use the check mark method to help illustrate your answer.
c. In terms of their collective profits, of the possible outcomes illustrated in the payoff table, is the Nash equilibrium the worst outcome for Kuwait and Venezuela?
Step by Step Answer:






