When fitting a polynomial to a set of paired data, we usually begin by fitting a straight
Question:
When fitting a polynomial to a set of paired data, we usually begin by fitting a straight line and using the method on page 339 to test the null hypothesis \(\beta_{1}=0\). Then we fit a second-degree polynomial and test whether it is worthwhile to carry the quadratic term by comparing \(\widehat{\sigma}_{1}^{2}\), the residual variance after fitting the straight line, with \(\widehat{\sigma}_{2}^{2}\), the residual variance after fitting the second-degree polynomial. Each of these residual variances is given by the formula
\[\frac{\sum(y-\widehat{y})^{2}}{\text { degrees of freedom }}=\frac{\operatorname{SSE}}{v}\]
with \(\widehat{y}\) determined, respectively, from the equation of the line and the equation of the second-degree polynomial. The decision whether to carry the quadratic term is based on the statistic
\[F=\frac{\mathrm{SSE}_{1}-\mathrm{SSE}_{2}}{\widehat{\sigma}_{2}^{2}}=\frac{v_{1} \widehat{\sigma}_{1}^{2}-v_{2} \widehat{\sigma}_{2}^{2}}{\widehat{\sigma}_{2}^{2}}\]
which (under the assumptions of Section 11.2 is a value of a random variable having the \(F\) distribution with 1 and \(n-3\) degrees of freedom.
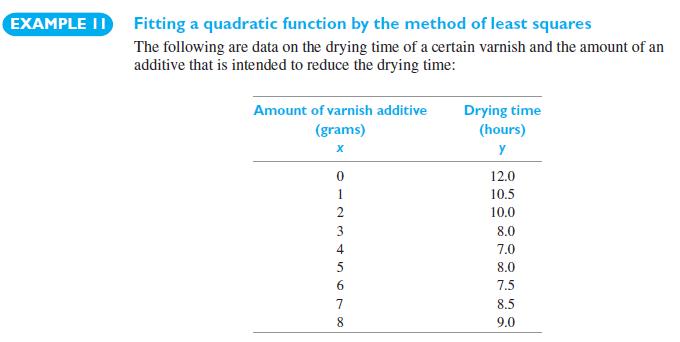
(a) Fit a straight line to the varnish-additive dryingtime data in Example 11, test the null hypothesis \(\beta_{1}=0\) at the 0.05 level of significance, and calculate \(\widehat{\sigma}_{1}^{2}\).
(b) Using the result in the varnish-additive example, calculate \(\widehat{\sigma}_{2}^{2}\) for the given data and test at the 0.05 level whether we should carry the quadratic term. That we could continue this procedure and test whether to carry a cubic term by means of a corresponding comparison of residual variances. Then we could test whether to carry a fourth-degree term, and so on. It is customary to terminate this procedure after two successive steps have not produced significant results.)
Data From Example 11

Step by Step Answer:

Probability And Statistics For Engineers
ISBN: 9780134435688
9th Global Edition
Authors: Richard Johnson, Irwin Miller, John Freund





