Consider a country operating under fixed exchange rates. The IS curve is given by relation (20.1) [
Question:
Consider a country operating under fixed exchange rates. The IS curve is given by relation (20.1)
\[
\begin{array}{r}
Y=Y\left(\frac{\overline{E P}}{P^{*}}, G, T, i^{*}-\pi^{e}, Y^{*}ight) \\
(-,+,-, \quad-, \quad+)
\end{array}
\]
a. Explain the term \(\left(i^{*}-\pi^{e}ight)\). Why does the foreign nominal interest rate appear in the relation?
b. Explain why when \(\frac{\bar{E} P}{P^{*}}\) increases, the IS curve shifts left.
c. In the following table, how is the real exchange rate evolving from period 1 to period 5? What is domestic inflation? What is foreign inflation? Draw an IS-LM diagram with the \(I S\) curve in period 1 and the \(I S\) curve in period 5.
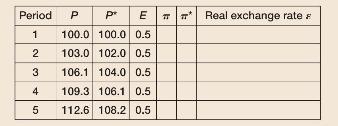
d. In the following table, how is the real exchange rate evolving from period 1 to period 5 ? What is domestic inflation? What is foreign inflation? Draw an IS-LM diagram with the IS curve in period 1 and the IS curve in period 5. 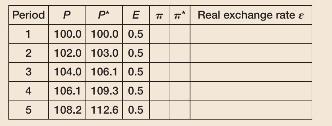
e. In the table that follows, how is the real exchange rate evolving from period 1 to period 4 ? What is domestic inflation? What is foreign inflation? What happened between Period 4 and Period 5? Draw an IS-LM diagram with the IS curve in period 1 and the IS curve in period 5.
Step by Step Answer:





