Gina lives in Chicago and very much enjoys traveling by air to see her mother in Italy.
Question:
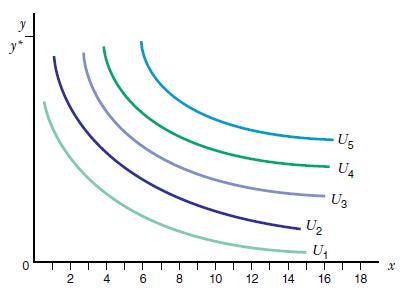
Gina lives in Chicago and very much enjoys traveling by air to see her mother in Italy. On the accompanying graph, x denotes her number of round trips to Italy each year. The composite good y measures her annual consumption of other goods; the price of the composite good is py, which is constant in this problem. Several indifference curves from her preference map are drawn, with levels of utility U1 < U2 < U3 < U4 < U5. If she spends all her income on the composite good, she can purchase y* units, as shown in the graph. When the initial price of air travel is $1,000, she can purchase as many as 18 round trips if she spends all her income on air travel to Italy.
a) Make a copy of the graph, and use it to determine the income and substitution effects on the number of round trips Gina makes as the price of a round trip increases from $1,000 to $3,000. Clearly label these effects on the graph.
b) Using the graph, estimate the numerical size of the compensating variation associated with the price increase. You may refer to the graph to explain your answer.
c) Will the consumer surplus measured using Gina’s demand for air travel to Italy provide an exact measure of the monetary value she associates with the price increase?
In a sentence, explain why or why not.
Step by Step Answer:






