A water treatment plant deals with a constant influx Q of polluted water with pollutant concentration s
Question:
A water treatment plant deals with a constant influx Q of polluted water with pollutant concentration s0. The treatment tank contains bacteria which consume the pollutant and protozoa which feed on the bacteria, thus keeping the bacteria from increasing too rapidly and overwhelming the system. If the concentration of the bacteria and the protozoa are denoted by b and p the system is governed by the differential equations
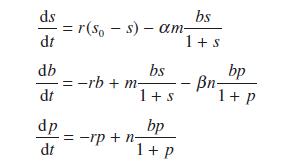
Write a program to solve these equations numerically. Measurements have determined that the (biological) parameters α, m, β and n have the values 0.5, 1.0, 0.8 and 0.1 respectively. The parameter r is a measure of the inflow rate of polluted water and s0 is the level of pollutant. Using the initial conditions s(0) = 0, b(0) = 0.2 and p(0) = 0.05 determine the final steady level of pollutant if r = 0.05 and s0 = 0.4. What effect does doubling the inflow rate (r) have?
Step by Step Answer:






