The Euler-Lagrange equation (16.14) is used in a field theory context in this chapter, but it is
Question:
The Euler-Lagrange equation (16.14) is used in a field theory context in this chapter, but it is applicable to a broad range of problems. Show that inserting a Lagrangian \(L(x, \dot{x})=\frac{1}{2} \dot{m}^{2}-V(x)\) in Eq. (16.14) leads to Newton's second law of motion.
Data from Eq. 16.14
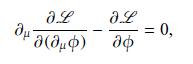
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Symmetry Broken Symmetry And Topology In Modern Physics A First Course
ISBN: 9781316518618
1st Edition
Authors: Mike Guidry, Yang Sun
Question Posted:





