Question: Create a list maintaining program: A program that allows the user to add, remove, print, and find different items in the list, interactively. Here is
Create a list maintaining program:
A program that allows the user to add, remove, print, and find different items in the list, interactively. Here is a sample program:

To add an item, the program will need to utilize the append method (Figure 1). To remove an item, use the remove method (Figure 1.), to find an item, use the membership operator (Figure 2.). To print the values, traverse the list with a loop shown in the example in (Figure 3. ). Use a sentinel loop pattern to control the execution of the program (see Figures 4 and 5.) using Q as the sentinel value.
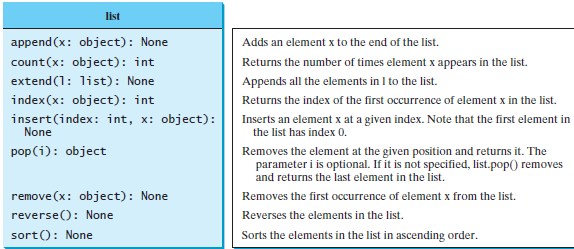 ---------FIGURE 1.
---------FIGURE 1.
 ----------FIGURE 2.
----------FIGURE 2.
 ------FIGURE 3.
------FIGURE 3.
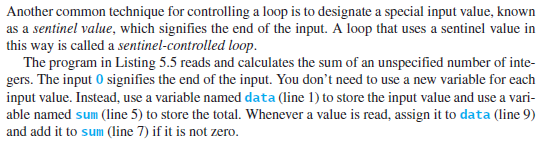 --------FIGURE 4.
--------FIGURE 4.
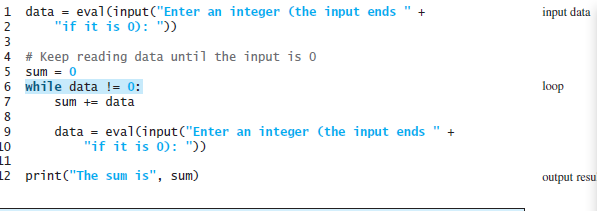 --------FIGURE 5.
--------FIGURE 5.
Menu: A)dd, R)emove, F)ind, P)rint, Q)uit: A Enter item to add: Buy milk Menu: A)dd, R)emove, F)ind, P)rint, Q)uit: A Enter item to add : Buy eggs Menu: A)dd, R)emove, F)ind, P)rint, Quit: A Enter item to add: Buy bread Menu: A)dd, R)emove, F)ind, P)rint, Q)uit: P List of items 1. Buy milk 2. Buy eggs 3. Buy bread Menu: A)dd, R)emove, F)ind, P)rint, Q)uit: R Enter item to remove: Buy milk Menu: A)dd, R)emove, F)ind, Print, Q)uit: P List of items 1. Buy eggs 2. Buy bread Menu: A)dd, R)emove, F)ind, Print, Q)uit: F What item to find: Buy milk Buy milk' is not in the list. list append(x: object): None count(x: object): int extend(1: list): None index(x: object): int insert(index: int, x: object): None pop(i): object Adds an element x to the end of the list. Returns the number of times element x appears in the list. Appends all the elements in I to the list. Returns the index of the first occurrence of element x in the list. Inserts an element x at a given index. Note that the first element in the list has index 0. Removes the element at the given position and returns it. The parameter i is optional. If it is not specified, list.pop removes and returns the last element in the list. Removes the first occurrence of element x from the list. Reverses the elements in the list. Sorts the elements in the list in ascending order. remove(x: object): None reverse(): None sortO: None You can determine whether an element is in a list by using the in or not in operator. For xample: >>> list1 = [2, 3, 5, 2, 33, 21] >>> 2 in listi True The elements in a Python list are iterable. Python supports a convenient for loop, which enables you to traverse the list sequentially without using an index variable. For example, the following code displays all the elements in the list myList: for u in mylist: print(u) You can read the code as, For each element u in myList, print it." You still have to use an index variable if you wish to traverse the list in a different order or change the elements in the list. For example, the following code displays the elements at odd- numbered positions. for i in range(0, len(myList), 2): print(myList[i]) Another common technique for controlling a loop is to designate a special input value, known as a sentinel value, which signifies the end of the input. A loop that uses a sentinel value in this way is called a sentinel-controlled loop. The program in Listing 5.5 reads and calculates the sum of an unspecified number of inte- gers. The input 0 signifies the end of the input. You don't need to use a new variable for each input value. Instead, use a variable named data (line 1) to store the input value and use a vari- able named sum (line 5) to store the total. Whenever a value is read, assign it to data (line 9) and add it to sum (line 7) if it is not zero. input data 1 data = eval(input("Enter an integer (the input ends " + 2 "if it is 0): ")) # Keep reading data until the input is o 5 sum = 0 6 while data != 0; sum += data data = eval(input("Enter an integer (the input ends " + 10 "if it is 0): ")) 11 12 print("The sum is", sum) HNmti00OON loop output resu
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


