Question: Please answer this question with extreme detail for an immediate thumbs up. I don't get credit unless it is detailed please help. Thank you for
Please answer this question with extreme detail for an immediate thumbs up. I don't get credit unless it is detailed please help. Thank you for your time in advance.
REQUIRED TEXT POSTED WITH QUESTION
**please use Walmart as employer for part 2 and 3** 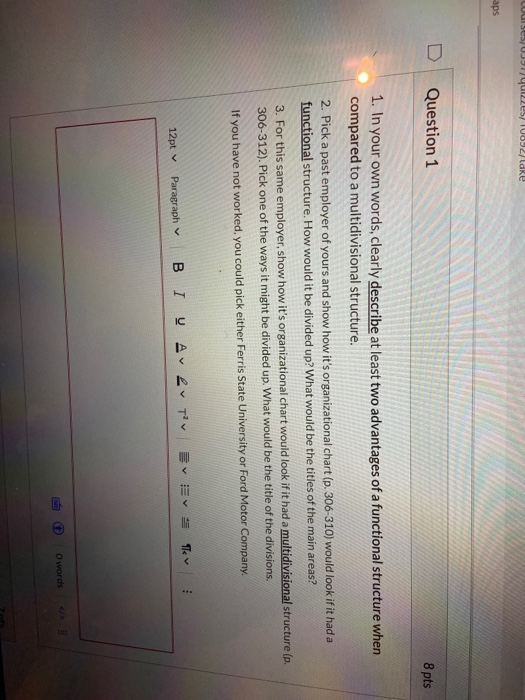









Question 1 This is all one question
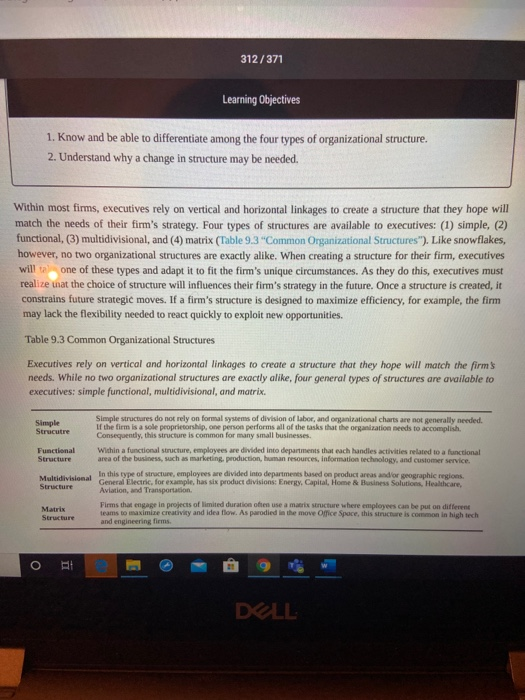
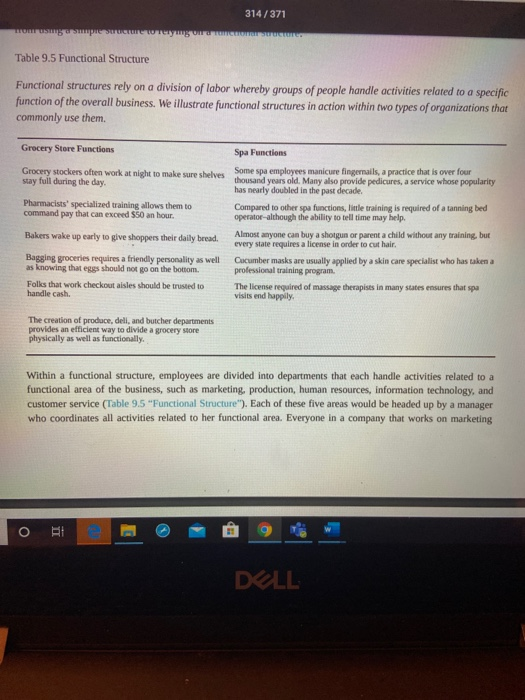
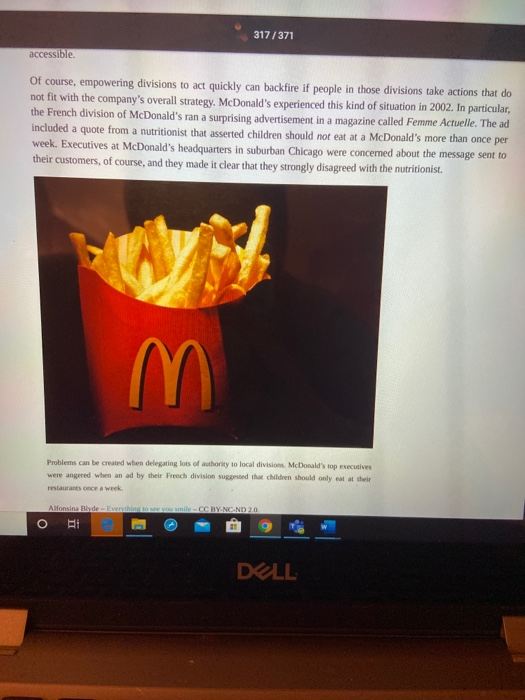
SED u ces Oy/lake aps D Question 1 8 pts 1. In your own words, clearly describe at least two advantages of a functional structure when compared to a multidivisional structure. 2. Pick a past employer of yours and show how it's organizational chart (p. 306-310) would look if it had a functional structure. How would it be divided up? What would be the titles of the main areas? 3. For this same employer, show how it's organizational chart would look if it had a multidivisional structure (p. 306-312). Pick one of the ways it might be divided up. What would be the title of the divisions. If you have not worked, you could pick either Ferris State University or Ford Motor Company E : 12pt Paragraph B IV ALT the words / 312/371 Learning Objectives 1. Know and be able to differentiate among the four types of organizational structure. 2. Understand why a change in structure may be needed. Within most firms, executives rely on vertical and horizontal linkages to create a structure that they hope will match the needs of their firm's strategy. Four types of structures are available to executives: (1) simple, (2) functional, (3) multidivisional, and (4) matrix (Table 9.3 "Common Organizational Structures"). Like snowflakes, however, no two organizational structures are exactly alike. When creating a structure for their firm, executives will one of these types and adapt it to fit the firm's unique circumstances. As they do this, executives must realize that the choice of structure will influences their firm's strategy in the future. Once a structure is created, it constrains future strategic moves. If a firm's structure is designed to maximize efficiency, for example, the firm may lack the flexibility needed to react quickly to exploit new opportunities. Table 9.3 Common Organizational Structures Executives rely on vertical and horizontal linkages to create a structure that they hope will match the firm needs. While no two organizational structures are exactly alike, four general types of structures are available to executives: simple functional, multidivisional, and matrix. Simple Strucutre Simple structures do not rely on formal systems of division of labor, and organizational charts are not generally needed If the firm is a sole proprietorship, one person performs all of the tasks that the organization needs to accomplish Consequently, this structure is common for many small businesses. Within a functional structure, employees are divided into departments that each handles activities related to a functional area of the business, such as marketing production, human resources, information technology, and customer service Functional Structure in this employee divided into departments based on te r apher General Electric, for example, has six product divisions Energy Capital Home & Business Solutions Healthcare Aviation, and Transportation Firms that engage in projects of limited duration of use a mastructure where employees can be put on differee teams to maximize creativity and idea fow. As parodied in the move Office Space, this is o n high tech and engineering fems. Matrix DELL 313/371 9.3 CREATING AN ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE. 307 Simple Structure Many organizations start out with a simple structure. In this type of structure, an organizational chart is usually not needed. Simple structures do not rely on formal systems of division of labor (Table 9.4 "Simple Structure"). If the firm is a sole proprietorship, one person performs all the tasks the organization needs to accomplish. For example, on the TV series The Simpsons, both bar owner Moe Szyslak and the Comic Book Guy are shown handling all aspects of their respective businesses. Table 9.4 Simple Structure Most small businesses begin with a simple structure where one person or a small set of people share the tasks needed to accomplish the firm goals with relatively little formalized division of labor. We Illustrate a number of businesses that commonly rely upon a simple structure below. Need a few dollars totide you over? You may want to pawn your care coin collection. The pawn shop's simple structure will mean that the same person values your coins, decides how much money you can borrow, and writes up your paperwork. The reality show Miami Ink illustrates how a tattoo parlor's simple structure governs a colorful set of tattoo artists who create body art for their patrons. Architects often also act as marketers and accountants when drafting their small business plans. Bait shop owners generally do not dive deep into their pockets to pay for additional personnel as many are owner operated When a dry cleaner is family owned as many are, all members of the family pitch in as needed to clean clothing and wait on customers There is flexibility in the management of many yoga Studios given the laid back management style often embraced. Instrument dealers may create beautiful music, but they rarely create complex organizational structures. "Bridezillas" are an occupational hazard for bridal shops, but these shops are generally able to avoid the complexity associated with other organizational structures You DOLL 313/371 You You You You You You vou You You you You You There is a good reason most sole proprietors do not bother creating formal organizational charts. If the firm consists of more than one person, tasks tend to be distributed among them in an informal manner rather than each person developing a narrow area of specialization. In a family run restaurant or bed and breakfast for example, each person must contribute as needed to tasks, such as cleaning restrooms, food preparation, and serving guests (hopefully not in that order). Meanwhile, strategic decision making in a simple structure tends to 308 - MASTERING STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT be highly centralized. Indeed, often the owner of the firm makes all the important decisions. Because there is little emphasis on hierarchy within a simple structure, organizations that use this type of structure tend to have very few rules and regulations. The process of evaluating and rewarding employees' performance also tends to be informal The informality of simple structures creates both advantages and disadvantages. On the plus side, the flexibility offered by simple structures encourages employees' creativity and individualism. Informality has potential DELL 314/371 300 MASTERING STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT be highly centralized. Indeed, often the owner of the firm makes all the important decisions. Because there is little emphasis on hierarchy within a simple structure, organizations that use this type of structure tend to have very few rules and regulations. The process of evaluating and rewarding employees' performance also tends to be informal The informality of simple structures creates both advantages and disadvantages. On the plus side, the flexibility offered by simple structures encourages employees' creativity and individualism. Informality has potential negative aspects, too. Important tasks may be ignored if no one person is specifically assigned accountability for them. A lack of clear guidance from the top of the organization can create confusion for employees, undermine their motivation, and make them dissatisfied with their jobs. Thus when relying on a simple structure, the owner of a firm must be sure to communicate often and openly with employees. Functional Structure As a small organization grows, the person in charge of it often finds that a simple structure is no longer adequate to meet the organization's needs. Organizations become more complex as they grow, and this can require more formal division of labor and a strong emphasis on hierarchy and vertical links. In many cases, these firms evolve from using a simple structure to relying on a functional structure. Table 9.5 Functional Structure Functional structures rely on a division of labor whereby groups of people handle activities related to a specific function of the overall business. We illustrate functional structures in action within two types of organizations that commonly use them. Grocery Store Functions Spa Functions Grocery stockers often work at night to make sure shelves stay full during the day. Some spa employees manicure fingernails, a practice that is over four thousand years old. Many also provide pedicures, a service whose popularity has nearly doubled in the past decade. Pharmacists' specialized training allows them to command pay that can exceed $50 an hour. Bakers wake up early to give shoppers their daily bread. Compared to other spa functions, line training is required of a tanning bed operator-although the ability to tell time may help Almost anyone can buy a shotgun or parent a child without any training, but every state requires a license in order to cut hair. Cucumber masks are usually applied by a skin care specialist who has taken a Bagging groceries requires a friendly personality as well DELL 314/371 p o yung Table 9.5 Functional Structure Functional structures rely on a division of labor whereby groups of people handle activities related to a specific function of the overall business. We illustrate functional structures in action within two types of organizations that commonly use them. Grocery Store Functions Spa Functions Grocery stockers often work at night to make sure shelves stay full during the day. Some spa employees manicure fingemails, a practice that is over four thousand years old. Many also provide pedicures, a service whose popularity has nearly doubled in the past decade. Compared to other spa functions, little training is required of a tanning bed operator-although the ability to tell time may help Pharmacists' specialized training allows them to command pay that can exceed $50 an hour. Bakers wake up early to give shoppers their daily bread. Bagging groceries requires a friendly personality as well as knowing that eggs should not go on the bottom. Folks that work checkout aisles should be trusted to handle cash. Almost anyone can buy a shotgun or parent a child without any training, but every state requires a license in order to cut hair. Cucumber masks are usually applied by a skin care specialist who has taken a professional training program. The license required of massage therapists in many states ensures that spa visits end happily The creation of produce, dell, and butcher departments provides an efficient way to divide a grocery store physically as well as functionally. Within a functional structure, employees are divided into departments that each handle activities related to a functional area of the business, such as marketing, production, human resources, information technology, and customer service (Table 9.5 "Functional Structure"). Each of these five areas would be headed up by a manager who coordinates all activities related to her functional area. Everyone in a company that works on marketing DOLL 315/371 9.3 CREATING AN ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE - 309 the company's products, for example, would report to the manager of the marketing department. The marketing managers and the managers in charge of the other four areas in tum would report to the chief executive officer. CEO Technology An example of a functional structure Using a functional structure creates advantages and disadvantages. An important benefit of adopting a functional structure is that each person tends to leam a great deal about his or her particular function. By being placed in a department that consists entirely of marketing professionals, an individual has a great opportunity to become an expert in marketing. Thus a functional structure tends to create highly skilled specialists. Second, grouping everyone that serves a particular function into one department tends to keep costs low and to create efficiency. Also, because all the people in a particular department share the same background training, they tend to get along with one another. In other words, conflicts within departments are relatively rare. Using a functional structure also has a significant downside: executing strategic changes can be very slow when compared with other structures. Suppose, for example, that a textbook publisher decides to introduce a new form of textbook that includes "scratch and sniff" photos that let students smell various products in addition to reading about them. If the publisher relies on a simple structure, the leader of the firm can simply assign someone to shepherd this unique new product through all aspects of the publication process If the publisher is organized using a functional structure, however, every department in the organization will have to be intimately involved in the creation of the new textbooks. Because the new product lies outside each department's routines, it may become lost in the proverbial shuffle. And unfortunately for the books authors, the publication process will be halted whenever a functional area does not live up to its responsibilities in a timely OPEN DELL F9 F10 315/371 with one another. In other words, conflicts within departments are relatively rare. Using a functional structure also has a significant downside: executing strategic changes can be very slow when compared with other structures. Suppose, for example, that a textbook publisher decides to introduce a new form of textbook that includes "scratch and sniff" photos that let students smell various products in addition to reading about them. If the publisher relies on a simple structure, the leader of the firm can simply assign someone to shepherd this unique new product through all aspects of the publication process. If the publisher is organized using a functional structure, however, every department in the organization will have to be intimately involved in the creation of the new textbooks. Because the new product lies outside each department's routines, it may become lost in the proverbial shuffle. And unfortunately for the books' authors, the publication process will be halted whenever a functional area does not live up to its responsibilities in a timely manner. More generally, because functional structures are slow to execute change, they tend to work best for organizations that offer narrow and stable product lines. The specific functional departments that appear in an organizational chart vary across organizations that use functional structures. In the example offered earlier in this section, a firm was divided into five functional areas: (1) marketing, (2) production, (3) human resources (4) information technology, and (5) customer service. In the TV show The Office, a different approach to a functional structure is used at the Scranton, Pennsylvania, branch of Dunder Mifflin. As of 2009, the branch was divided into six functional areas: (1) sales, (2) warehouse, (3) quality control, (4) customer service, (5) human resources, and (6) accounting. A functional structure was a good fit for the branch at the time because its product line was limited to just selling office paper. 310. MASTERING STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT DELL 316/371 Dunder Mifflin (Functional Structure) Human Resources Contre Customer Service Warehouse The Scranton branch of Dunder Mifflin may be a dysfunctional organization, but it relies on a functional structure. M inion Store DELL 316/371 Multidivisional Structure Many organizations offer a wide variety of products and services. Some of these organizations sell their offerings across an array of geographic regions. These approaches require firms to be very responsive to customers' needs. Yet, as noted, functional structures tend to be fairly slow to change. As a result, many firms abandon the use of a functional structure as their offerings expand. Often the new choice is a multidivisional structure. In this type of structure, employees are divided into departments based on product areas and/or geographic regions. General Electric (GE) is an example of a company organized this way. As shown in the organization chart that accompanies this chapter's opening vignette, most of the company's employees belong to one of six product divisions (Energy, Capital, Home & Business Solutions, Health Care, Aviation, and Transportation) or to a division that is devoted to all GE's operations outside the United States (Global Growth & Operations). 9.3 CREATING AN ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE. 311 A big advantage of a multidivisional structure is that it allows a firm to act quickly. When GE makes a strategic move such as acquiring the well-support division of John Wood Group PLC, only the relevant division (in this case, Energy) needs to be involved in integrating the new unit into GE's hierarchy. In contrast, if GE was organized using a functional structure, the transition would be much slower because all the divisions in the company would need to be involved. A multidivisional structure also helps an organization to better serve customers' needs. In the summer of 2011, for example, GE's Capital division started to make real estate loans after exiting that market during the financial crisis of the late 2000s (Jacobus, 2011). Because one division of GE handles all the firm's loans, the wisdom and skill needed to decide when to reenter real estate lending was easily accessible. Of course, empowering divisions to act quickly can backfire if people in those divisions take actions that do not fit with the company's overall strategy. McDonald's experienced this kind of situation in 2002. In particular, ORI DELL 317/371 accessible. Of course, empowering divisions to act quickly can backfire if people in those divisions take actions that do not fit with the company's overall strategy. McDonald's experienced this kind of situation in 2002. In particular, the French division of McDonald's ran a surprising advertisement in a magazine called Femme Actuelle. The ad included a quote from a nutritionist that asserted children should not eat at a McDonald's more than once per week. Executives at McDonald's headquarters in suburban Chicago were concerned about the message sent to their customers, of course, and they made it clear that they strongly disagreed with the nutritionist. Problems can be created when delegating lots of authority to local divisions. McDonald's top executives were angered when an ad by their Prech division suggested the children should only eat at their restaurants once a week Alfonsina Blyde - Everything to see you smile-CC BYNC-ND 2.0 DELL - MyGX E Master X B Conter X Mastering Strategic Management,%203%20(4).pdf Problems can be created when delegating loss of authority to local divisions McDonald's top were red when and by the French division that daldren should only t s he Alfonsinalde- you -CC BY-NC-ND 20 Another downside of multidivisional structures is that they tend to be more costly to operate than functional Structures. While a functional structure offers the opportunity to gain efficiency by having just one department 312 - MASTERING STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT handle all activities in an area, such as marketing, a fim using a multidivisional structure needs to have marketing units within each of its divisions. In GE's case, for example, each of its seven divisions must develop marketing skills. Absorbing the extra expenses that are created reduces a firm's profit margin. GE's organizational chart highlights a way that firms can reduce some of these expenses: the centralization of some functional services. As shown in the organizational chart, departments devoted to important aspects of public relations, business development, legal, global research, human resources, and finance are maintained centrally to provide services to the six product divisions and the geographic division. By consolidating some human resource activities in one location, for example, GE creates efficiency and saves money, An additional benefit of such moves is that consistency is created across divisions. In 2011, for example, the Coca-Cola Company created an Office of Sustainability to coordinate sustainability Initiatives across the entire company, Bea Pere was named Coca-Cola's chief sustainability officer and was put in charge of the Office of Sustainability. At the time, Coca-Cola's chief executive officer Muhtar Kent noted that Coca-Cola had "made significant progress with our sustainability initiatives, but our current approach needs focus and better Integration (McWilliams, 2011). In other words, a department devoted to creating consistency across Coca coded DELL An additional benefit of such moves is that consistency is created across divisions. In 2011, for example, the Coca-Cola Company created an Office of Sustainability to coordinate sustainability initiatives across the entire company. Bea Perez was named Coca-Cola's chief sustainability officer and was put in charge of the Office of Sustainability. At the time, Coca-Cola's chief executive officer Muhtar Kent noted that Coca-Cola had "made significant progress with our sustainability initiatives, but our current approach needs focus and better Integration (McWilliams, 2011)." In other words, a department devoted to creating consistency across Coca. Cola's sustainability efforts was needed for Coca-Cola to meet its sustainability goals. Matrix Structure Within functional and multidivisional structures, vertical linkages between bosses and subordinates are the most elements. Matrix structures, in contrast, rely heavily on horizontal relationships (Ketchen & Short, 2011). In particular, these structures create cross-functional teams that each work on a different project. This offers several benefits: maximizing the organization's flexibility, enhancing communication across functional lines, and creating a spirit of teamwork and collaboration. A matrix structure can also help develop new managers. In particular, a person without managerial experience can be put in charge of a relatively small project as a test to see whether the person has a talent for leading others. Using a matrix structure can create difficulties too. One concern is that using a matrix structure violates the unity of command principle because each employee is assigned multiple bosses. Specifically, any given individual reports to a functional area supervisor as well as one or more project supervisors. This creates confusion for employees because they are left unsure about who should be giving them direction. Violating the unity of command principle also creates opportunities for unsavory employees to avoid responsibility by claiming to each supervisor that a different supervisor is currently depending on their efforts. The potential for conflicts arising between project managers within a matrix structure is another concem. Chances are that you have had some classes with professors who are excellent speakers while you have been forced to suffer through a semester of incomprehensible lectures in other classes. This mix of experiences reflects a fundamental reality of management in any organization, some workers are more talented and motivated than others. Within a matrix structure, each project manager naturally will want the best people in the company assigned to her project because their boss evaluates these managers based on how well their projects perform Because the best people are a scarce resource, infighting and politics can easily flare up around which people are DELL 318/371 W O MICIDIOTIV w ruchu person without managerial experience can be put in charge of a relatively small project as a test to see whether the person has a talent for leading others. Using a matrix structure can create difficulties too. One concern is that using a matrix structure violates the unity of command principle because each employee is assigned multiple bosses. Specifically, any given individual reports to a functional area supervisor as well as one or more project supervisors. This creates confusion for employees because they are left unsure about who should be giving them direction. Violating the unity of command principle also creates opportunities for unsavory employees to avoid responsibility by claiming to each supervisor that a different supervisor is currently depending on their efforts. The potential for conflicts arising between project managers within a matrix structure is another concem. Chances are that you have had some classes with professors who are excellent speakers while you have been forced to suffer through a semester of incomprehensible lectures in other classes. This mix of experiences reflects a fundamental reality of management: in any organization, some workers are more talented and motivated than others. Within a matrix structure, each project manager naturally will want the best people in the company assigned to her project because their boss evaluates these managers based on how well their projects perform. Because the best people are a scarce resource, infighting and politics can easily flare up around which people are assigned to each project. Given these problems, not every organization is a good candidate to use a matrix structure. Organizations such as 9.3 CREATING AN ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE. 313 engineering and consulting firms that need to maximize their flexibility to service projects of limited duration can benefit from the use of a matrix. Matrix structures are also used to organize research and development departments within many large corporations. In each of these settings, the benefits of organizing around teams are so great that they often outweigh the risks of doing so. O PA DELL SED u ces Oy/lake aps D Question 1 8 pts 1. In your own words, clearly describe at least two advantages of a functional structure when compared to a multidivisional structure. 2. Pick a past employer of yours and show how it's organizational chart (p. 306-310) would look if it had a functional structure. How would it be divided up? What would be the titles of the main areas? 3. For this same employer, show how it's organizational chart would look if it had a multidivisional structure (p. 306-312). Pick one of the ways it might be divided up. What would be the title of the divisions. If you have not worked, you could pick either Ferris State University or Ford Motor Company E : 12pt Paragraph B IV ALT the words / 312/371 Learning Objectives 1. Know and be able to differentiate among the four types of organizational structure. 2. Understand why a change in structure may be needed. Within most firms, executives rely on vertical and horizontal linkages to create a structure that they hope will match the needs of their firm's strategy. Four types of structures are available to executives: (1) simple, (2) functional, (3) multidivisional, and (4) matrix (Table 9.3 "Common Organizational Structures"). Like snowflakes, however, no two organizational structures are exactly alike. When creating a structure for their firm, executives will one of these types and adapt it to fit the firm's unique circumstances. As they do this, executives must realize that the choice of structure will influences their firm's strategy in the future. Once a structure is created, it constrains future strategic moves. If a firm's structure is designed to maximize efficiency, for example, the firm may lack the flexibility needed to react quickly to exploit new opportunities. Table 9.3 Common Organizational Structures Executives rely on vertical and horizontal linkages to create a structure that they hope will match the firm needs. While no two organizational structures are exactly alike, four general types of structures are available to executives: simple functional, multidivisional, and matrix. Simple Strucutre Simple structures do not rely on formal systems of division of labor, and organizational charts are not generally needed If the firm is a sole proprietorship, one person performs all of the tasks that the organization needs to accomplish Consequently, this structure is common for many small businesses. Within a functional structure, employees are divided into departments that each handles activities related to a functional area of the business, such as marketing production, human resources, information technology, and customer service Functional Structure in this employee divided into departments based on te r apher General Electric, for example, has six product divisions Energy Capital Home & Business Solutions Healthcare Aviation, and Transportation Firms that engage in projects of limited duration of use a mastructure where employees can be put on differee teams to maximize creativity and idea fow. As parodied in the move Office Space, this is o n high tech and engineering fems. Matrix DELL 313/371 9.3 CREATING AN ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE. 307 Simple Structure Many organizations start out with a simple structure. In this type of structure, an organizational chart is usually not needed. Simple structures do not rely on formal systems of division of labor (Table 9.4 "Simple Structure"). If the firm is a sole proprietorship, one person performs all the tasks the organization needs to accomplish. For example, on the TV series The Simpsons, both bar owner Moe Szyslak and the Comic Book Guy are shown handling all aspects of their respective businesses. Table 9.4 Simple Structure Most small businesses begin with a simple structure where one person or a small set of people share the tasks needed to accomplish the firm goals with relatively little formalized division of labor. We Illustrate a number of businesses that commonly rely upon a simple structure below. Need a few dollars totide you over? You may want to pawn your care coin collection. The pawn shop's simple structure will mean that the same person values your coins, decides how much money you can borrow, and writes up your paperwork. The reality show Miami Ink illustrates how a tattoo parlor's simple structure governs a colorful set of tattoo artists who create body art for their patrons. Architects often also act as marketers and accountants when drafting their small business plans. Bait shop owners generally do not dive deep into their pockets to pay for additional personnel as many are owner operated When a dry cleaner is family owned as many are, all members of the family pitch in as needed to clean clothing and wait on customers There is flexibility in the management of many yoga Studios given the laid back management style often embraced. Instrument dealers may create beautiful music, but they rarely create complex organizational structures. "Bridezillas" are an occupational hazard for bridal shops, but these shops are generally able to avoid the complexity associated with other organizational structures You DOLL 313/371 You You You You You You vou You You you You You There is a good reason most sole proprietors do not bother creating formal organizational charts. If the firm consists of more than one person, tasks tend to be distributed among them in an informal manner rather than each person developing a narrow area of specialization. In a family run restaurant or bed and breakfast for example, each person must contribute as needed to tasks, such as cleaning restrooms, food preparation, and serving guests (hopefully not in that order). Meanwhile, strategic decision making in a simple structure tends to 308 - MASTERING STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT be highly centralized. Indeed, often the owner of the firm makes all the important decisions. Because there is little emphasis on hierarchy within a simple structure, organizations that use this type of structure tend to have very few rules and regulations. The process of evaluating and rewarding employees' performance also tends to be informal The informality of simple structures creates both advantages and disadvantages. On the plus side, the flexibility offered by simple structures encourages employees' creativity and individualism. Informality has potential DELL 314/371 300 MASTERING STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT be highly centralized. Indeed, often the owner of the firm makes all the important decisions. Because there is little emphasis on hierarchy within a simple structure, organizations that use this type of structure tend to have very few rules and regulations. The process of evaluating and rewarding employees' performance also tends to be informal The informality of simple structures creates both advantages and disadvantages. On the plus side, the flexibility offered by simple structures encourages employees' creativity and individualism. Informality has potential negative aspects, too. Important tasks may be ignored if no one person is specifically assigned accountability for them. A lack of clear guidance from the top of the organization can create confusion for employees, undermine their motivation, and make them dissatisfied with their jobs. Thus when relying on a simple structure, the owner of a firm must be sure to communicate often and openly with employees. Functional Structure As a small organization grows, the person in charge of it often finds that a simple structure is no longer adequate to meet the organization's needs. Organizations become more complex as they grow, and this can require more formal division of labor and a strong emphasis on hierarchy and vertical links. In many cases, these firms evolve from using a simple structure to relying on a functional structure. Table 9.5 Functional Structure Functional structures rely on a division of labor whereby groups of people handle activities related to a specific function of the overall business. We illustrate functional structures in action within two types of organizations that commonly use them. Grocery Store Functions Spa Functions Grocery stockers often work at night to make sure shelves stay full during the day. Some spa employees manicure fingernails, a practice that is over four thousand years old. Many also provide pedicures, a service whose popularity has nearly doubled in the past decade. Pharmacists' specialized training allows them to command pay that can exceed $50 an hour. Bakers wake up early to give shoppers their daily bread. Compared to other spa functions, line training is required of a tanning bed operator-although the ability to tell time may help Almost anyone can buy a shotgun or parent a child without any training, but every state requires a license in order to cut hair. Cucumber masks are usually applied by a skin care specialist who has taken a Bagging groceries requires a friendly personality as well DELL 314/371 p o yung Table 9.5 Functional Structure Functional structures rely on a division of labor whereby groups of people handle activities related to a specific function of the overall business. We illustrate functional structures in action within two types of organizations that commonly use them. Grocery Store Functions Spa Functions Grocery stockers often work at night to make sure shelves stay full during the day. Some spa employees manicure fingemails, a practice that is over four thousand years old. Many also provide pedicures, a service whose popularity has nearly doubled in the past decade. Compared to other spa functions, little training is required of a tanning bed operator-although the ability to tell time may help Pharmacists' specialized training allows them to command pay that can exceed $50 an hour. Bakers wake up early to give shoppers their daily bread. Bagging groceries requires a friendly personality as well as knowing that eggs should not go on the bottom. Folks that work checkout aisles should be trusted to handle cash. Almost anyone can buy a shotgun or parent a child without any training, but every state requires a license in order to cut hair. Cucumber masks are usually applied by a skin care specialist who has taken a professional training program. The license required of massage therapists in many states ensures that spa visits end happily The creation of produce, dell, and butcher departments provides an efficient way to divide a grocery store physically as well as functionally. Within a functional structure, employees are divided into departments that each handle activities related to a functional area of the business, such as marketing, production, human resources, information technology, and customer service (Table 9.5 "Functional Structure"). Each of these five areas would be headed up by a manager who coordinates all activities related to her functional area. Everyone in a company that works on marketing DOLL 315/371 9.3 CREATING AN ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE - 309 the company's products, for example, would report to the manager of the marketing department. The marketing managers and the managers in charge of the other four areas in tum would report to the chief executive officer. CEO Technology An example of a functional structure Using a functional structure creates advantages and disadvantages. An important benefit of adopting a functional structure is that each person tends to leam a great deal about his or her particular function. By being placed in a department that consists entirely of marketing professionals, an individual has a great opportunity to become an expert in marketing. Thus a functional structure tends to create highly skilled specialists. Second, grouping everyone that serves a particular function into one department tends to keep costs low and to create efficiency. Also, because all the people in a particular department share the same background training, they tend to get along with one another. In other words, conflicts within departments are relatively rare. Using a functional structure also has a significant downside: executing strategic changes can be very slow when compared with other structures. Suppose, for example, that a textbook publisher decides to introduce a new form of textbook that includes "scratch and sniff" photos that let students smell various products in addition to reading about them. If the publisher relies on a simple structure, the leader of the firm can simply assign someone to shepherd this unique new product through all aspects of the publication process If the publisher is organized using a functional structure, however, every department in the organization will have to be intimately involved in the creation of the new textbooks. Because the new product lies outside each department's routines, it may become lost in the proverbial shuffle. And unfortunately for the books authors, the publication process will be halted whenever a functional area does not live up to its responsibilities in a timely OPEN DELL F9 F10 315/371 with one another. In other words, conflicts within departments are relatively rare. Using a functional structure also has a significant downside: executing strategic changes can be very slow when compared with other structures. Suppose, for example, that a textbook publisher decides to introduce a new form of textbook that includes "scratch and sniff" photos that let students smell various products in addition to reading about them. If the publisher relies on a simple structure, the leader of the firm can simply assign someone to shepherd this unique new product through all aspects of the publication process. If the publisher is organized using a functional structure, however, every department in the organization will have to be intimately involved in the creation of the new textbooks. Because the new product lies outside each department's routines, it may become lost in the proverbial shuffle. And unfortunately for the books' authors, the publication process will be halted whenever a functional area does not live up to its responsibilities in a timely manner. More generally, because functional structures are slow to execute change, they tend to work best for organizations that offer narrow and stable product lines. The specific functional departments that appear in an organizational chart vary across organizations that use functional structures. In the example offered earlier in this section, a firm was divided into five functional areas: (1) marketing, (2) production, (3) human resources (4) information technology, and (5) customer service. In the TV show The Office, a different approach to a functional structure is used at the Scranton, Pennsylvania, branch of Dunder Mifflin. As of 2009, the branch was divided into six functional areas: (1) sales, (2) warehouse, (3) quality control, (4) customer service, (5) human resources, and (6) accounting. A functional structure was a good fit for the branch at the time because its product line was limited to just selling office paper. 310. MASTERING STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT DELL 316/371 Dunder Mifflin (Functional Structure) Human Resources Contre Customer Service Warehouse The Scranton branch of Dunder Mifflin may be a dysfunctional organization, but it relies on a functional structure. M inion Store DELL 316/371 Multidivisional Structure Many organizations offer a wide variety of products and services. Some of these organizations sell their offerings across an array of geographic regions. These approaches require firms to be very responsive to customers' needs. Yet, as noted, functional structures tend to be fairly slow to change. As a result, many firms abandon the use of a functional structure as their offerings expand. Often the new choice is a multidivisional structure. In this type of structure, employees are divided into departments based on product areas and/or geographic regions. General Electric (GE) is an example of a company organized this way. As shown in the organization chart that accompanies this chapter's opening vignette, most of the company's employees belong to one of six product divisions (Energy, Capital, Home & Business Solutions, Health Care, Aviation, and Transportation) or to a division that is devoted to all GE's operations outside the United States (Global Growth & Operations). 9.3 CREATING AN ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE. 311 A big advantage of a multidivisional structure is that it allows a firm to act quickly. When GE makes a strategic move such as acquiring the well-support division of John Wood Group PLC, only the relevant division (in this case, Energy) needs to be involved in integrating the new unit into GE's hierarchy. In contrast, if GE was organized using a functional structure, the transition would be much slower because all the divisions in the company would need to be involved. A multidivisional structure also helps an organization to better serve customers' needs. In the summer of 2011, for example, GE's Capital division started to make real estate loans after exiting that market during the financial crisis of the late 2000s (Jacobus, 2011). Because one division of GE handles all the firm's loans, the wisdom and skill needed to decide when to reenter real estate lending was easily accessible. Of course, empowering divisions to act quickly can backfire if people in those divisions take actions that do not fit with the company's overall strategy. McDonald's experienced this kind of situation in 2002. In particular, ORI DELL 317/371 accessible. Of course, empowering divisions to act quickly can backfire if people in those divisions take actions that do not fit with the company's overall strategy. McDonald's experienced this kind of situation in 2002. In particular, the French division of McDonald's ran a surprising advertisement in a magazine called Femme Actuelle. The ad included a quote from a nutritionist that asserted children should not eat at a McDonald's more than once per week. Executives at McDonald's headquarters in suburban Chicago were concerned about the message sent to their customers, of course, and they made it clear that they strongly disagreed with the nutritionist. Problems can be created when delegating lots of authority to local divisions. McDonald's top executives were angered when an ad by their Prech division suggested the children should only eat at their restaurants once a week Alfonsina Blyde - Everything to see you smile-CC BYNC-ND 2.0 DELL - MyGX E Master X B Conter X Mastering Strategic Management,%203%20(4).pdf Problems can be created when delegating loss of authority to local divisions McDonald's top were red when and by the French division that daldren should only t s he Alfonsinalde- you -CC BY-NC-ND 20 Another downside of multidivisional structures is that they tend to be more costly to operate than functional Structures. While a functional structure offers the opportunity to gain efficiency by having just one department 312 - MASTERING STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT handle all activities in an area, such as marketing, a fim using a multidivisional structure needs to have marketing units within each of its divisions. In GE's case, for example, each of its seven divisions must develop marketing skills. Absorbing the extra expenses that are created reduces a firm's profit margin. GE's organizational chart highlights a way that firms can reduce some of these expenses: the centralization of some functional services. As shown in the organizational chart, departments devoted to important aspects of public relations, business development, legal, global research, human resources, and finance are maintained centrally to provide services to the six product divisions and the geographic division. By consolidating some human resource activities in one location, for example, GE creates efficiency and saves money, An additional benefit of such moves is that consistency is created across divisions. In 2011, for example, the Coca-Cola Company created an Office of Sustainability to coordinate sustainability Initiatives across the entire company, Bea Pere was named Coca-Cola's chief sustainability officer and was put in charge of the Office of Sustainability. At the time, Coca-Cola's chief executive officer Muhtar Kent noted that Coca-Cola had "made significant progress with our sustainability initiatives, but our current approach needs focus and better Integration (McWilliams, 2011). In other words, a department devoted to creating consistency across Coca coded DELL An additional benefit of such moves is that consistency is created across divisions. In 2011, for example, the Coca-Cola Company created an Office of Sustainability to coordinate sustainability initiatives across the entire company. Bea Perez was named Coca-Cola's chief sustainability officer and was put in charge of the Office of Sustainability. At the time, Coca-Cola's chief executive officer Muhtar Kent noted that Coca-Cola had "made significant progress with our sustainability initiatives, but our current approach needs focus and better Integration (McWilliams, 2011)." In other words, a department devoted to creating consistency across Coca. Cola's sustainability efforts was needed for Coca-Cola to meet its sustainability goals. Matrix Structure Within functional and multidivisional structures, vertical linkages between bosses and subordinates are the most elements. Matrix structures, in contrast, rely heavily on horizontal relationships (Ketchen & Short, 2011). In particular, these structures create cross-functional teams that each work on a different project. This offers several benefits: maximizing the organization's flexibility, enhancing communication across functional lines, and creating a spirit of teamwork and collaboration. A matrix structure can also help develop new managers. In particular, a person without managerial experience can be put in charge of a relatively small project as a test to see whether the person has a talent for leading others. Using a matrix structure can create difficulties too. One concern is that using a matrix structure violates the unity of command principle because each employee is assigned multiple bosses. Specifically, any given individual reports to a functional area supervisor as well as one or more project supervisors. This creates confusion for employees because they are left unsure about who should be giving them direction. Violating the unity of command principle also creates opportunities for unsavory employees to avoid responsibility by claiming to each supervisor that a different supervisor is currently depending on their efforts. The potential for conflicts arising between project managers within a matrix structure is another concem. Chances are that you have had some classes with professors who are excellent speakers while you have been forced to suffer through a semester of incomprehensible lectures in other classes. This mix of experiences reflects a fundamental reality of management in any organization, some workers are more talented and motivated than others. Within a matrix structure, each project manager naturally will want the best people in the company assigned to her project because their boss evaluates these managers based on how well their projects perform Because the best people are a scarce resource, infighting and politics can easily flare up around which people are DELL 318/371 W O MICIDIOTIV w ruchu person without managerial experience can be put in charge of a relatively small project as a test to see whether the person has a talent for leading others. Using a matrix structure can create difficulties too. One concern is that using a matrix structure violates the unity of command principle because each employee is assigned multiple bosses. Specifically, any given individual reports to a functional area supervisor as well as one or more project supervisors. This creates confusion for employees because they are left unsure about who should be giving them direction. Violating the unity of command principle also creates opportunities for unsavory employees to avoid responsibility by claiming to each supervisor that a different supervisor is currently depending on their efforts. The potential for conflicts arising between project managers within a matrix structure is another concem. Chances are that you have had some classes with professors who are excellent speakers while you have been forced to suffer through a semester of incomprehensible lectures in other classes. This mix of experiences reflects a fundamental reality of management: in any organization, some workers are more talented and motivated than others. Within a matrix structure, each project manager naturally will want the best people in the company assigned to her project because their boss evaluates these managers based on how well their projects perform. Because the best people are a scarce resource, infighting and politics can easily flare up around which people are assigned to each project. Given these problems, not every organization is a good candidate to use a matrix structure. Organizations such as 9.3 CREATING AN ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE. 313 engineering and consulting firms that need to maximize their flexibility to service projects of limited duration can benefit from the use of a matrix. Matrix structures are also used to organize research and development departments within many large corporations. In each of these settings, the benefits of organizing around teams are so great that they often outweigh the risks of doing so. O PA DELL part 1) In your own words, clearly describe at least two advantages of a functional structure when compared to multidivisional structure.
part 2) pick a past employer of yours and show how it's organizational chart (p. 306-310) would look if it had a functional structure. How would it be divided up? What would be the titles of the main areas?
part 3) for this same employer, show how it's organizational chart would look if it had a multidivisional structure (p. 306-312). pick one of the ways it might be divided up. What would be the title of the divisions.
*For an employer please use either Walmart or Ford motor company*
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


