Suppose you are an engineering geologist designing a nuclear waste repository in the Rohan Tuff (see Problem
Question:
Suppose you are an engineering geologist designing a nuclear waste repository in the Rohan Tuff (see Problem 13.4). Figure 13.11 shows the general plan of the repository. It will be a large room, the ceiling of which is to be 20 m deep within the tuff. During excavation of the repository, cylindrical pillars of tuff 5 m in diameter will be left in place to support the 20 m of overburden. Determine the maximum spacing of pillars (center to center) sufficient to support the overlying tuff. The density of the tuff is 2.0 g = cm3. Assume that the confining pressure on the pillars is atmospheric pressure, 0.1 MPa. Clearly show how you got your answer.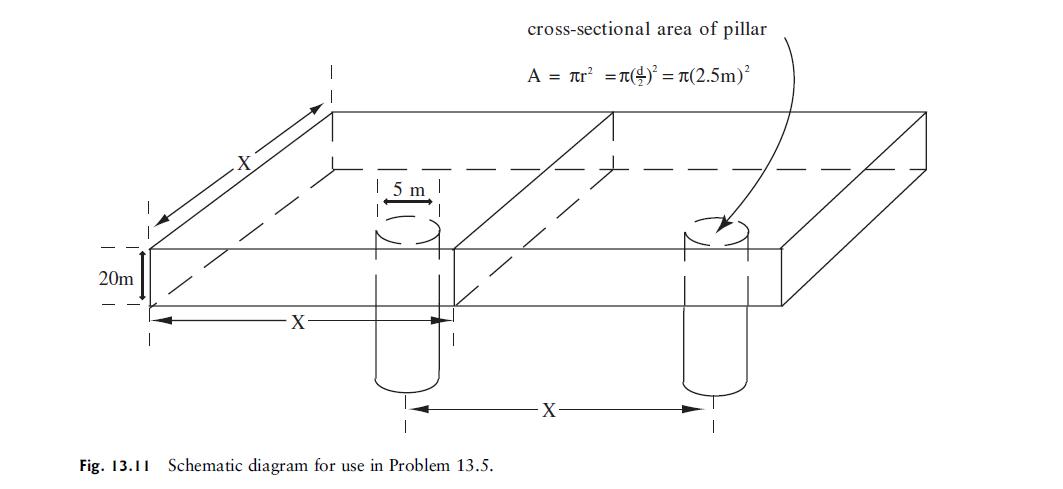
Problem 13.4
The results of four fracture experiments on samples of Rohan Tuff are recorded in the table below.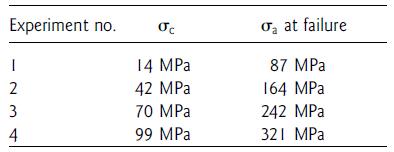
1. Draw Mohr circles for each experiment, and draw the failure envelope.
2. Determine the Coulomb coefficient of the Rohan Tuff.
3. Determine the angle u that the fracture plane is predicted to form with the σ3 direction when a sample of Rohan Tuff fractures.
Step by Step Answer:

Structural Analysis And Synthesis A Laboratory Course In Structural Geology
ISBN: 9781405116527
3rd Edition
Authors: Stephen M. Rowland, Ernest M. Duebendorfer, Ilsa M. Schiefelbein




