When a human takes a breath, the inhaled air flows through the nostrils and trachea before splitting
Question:
When a human takes a breath, the inhaled air flows through the nostrils and trachea before splitting into two primary bronchial tubes. The primary tubes further split to form smaller tubes, and eventually the air passages end in sacs, called alveoli. In the alveoli, oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged with the blood. The typical trachea is 2 cm in diameter; the right primary bronchial tube has a diameter of 12mm and that of the left is 10.0 mm. The average adult takes 12 breaths per minute, with each breath taking in about 0.5 L of air at ambient conditions, which may be taken to be 1.0 atm and 25°C.
The velocities of air in the two bronchial tubes are related by the approximation
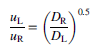
where uL and uR are velocities in the left and right bronchial tubes and DL and DR are the diameters of the left and right tubes, respectively. The temperature of the air in the bronchial tubes may be assumed to have reached 37°C. Recognizing that half of a breathing cycle is exhaling, estimate the mass flow rates and the velocities of air flowing through the trachea and each of the primary bronchial tubes.
Step by Step Answer:

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes
ISBN: 978-1119498759
4th edition
Authors: Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard





