Cosmological redshift the expansion of the universe is often represented with a drawing like Figure a. In
Question:
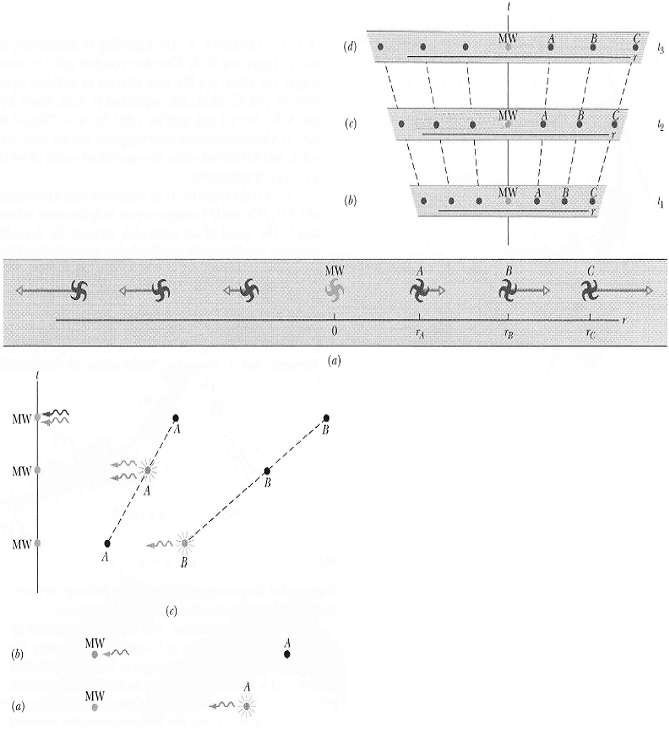
Cosmological redshift the expansion of the universe is often represented with a drawing like Figure a. In that figure, we are located at the symbol labeled MW (for the Milky Way galaxy), at the origin of an r axis that extends radially away from us in any direction. Other, very distant galaxies are also represented. Superimposed on their symbols are their velocity vectors as inferred from the redshift of the light reaching us from the galaxies? In accord with Hubble's law, the speed of each galaxy is proportional to its distance from us. Such drawings can be misleading because they imply (1) that the redshift are due to the motions of galaxies relative to us, as they rush away from us through static (stationary) space, and (2) that we are at the center of all this motion. Actually, the expansion of the universe and the increased separation of the galaxies are due not to an outward rush of the galaxies into pre-existing space but to an expansion of space itself throughout the universe. Space is dynamic, not static. Figures b, c, and d show a different way of representing the universe and its expansion. Each part of the figure gives part of a one-dimensional section of the universe (along an r axis); the other two spatial dimensions of the universe are not shown. Each of the three parts of the figure shows the Milky Way and six other galaxies (represented by dots); the parts are positioned along a time axis, with time increasing upward. In part b, at the earliest time of the three parts, the Milky Way and the six other galaxies are represented as being relatively close to one another. As time progresses upward in the figures, space expands, causing the galaxies to move apart. Note that the figure parts are drawn relative to the Milky Way, and from that observation point all the other galaxies move away because of the expansion. However, there is nothing special about the Milky Way-the galaxies also move away from any other observation point we might have chosen. Figures a and b focus on just the Milky Way galaxy and one of the other galaxies, galaxy A, at two particular times during the expansion. In part a, galaxy A is a distance r from the Milky Way and is emitting a light wave of wavelength λ. In part b, after a time interval Δ t, that light wave is being detected at Barth. Let us represent the universe's expansion rate per unit length of space with a, which we assume to be constant during time interval Δ t. Then during Δ t, every unit length of space (say, every meter) expands by an amount a Δ t; hence, a distance r expands by ra Δ t. The light wave of Figures a and b travels at speed c from galaxy A to Earth.
(a) Show that Δ t = r/ c ?? r α. The detected wavelength λ' the light is greater than the emitted wavelength l because space expanded during time interval Δ t. This increase in wavelength is called the cosmological redshift; it is not a Doppler effect.
(b) Show that the change in wavelength Δ λ (= λ' - λ) is given by Δ λ / λ = r α / c ?? r α
(c) Expand the right side of this equation using the binomial expansion (given in Appendix E).
(d) If you retain only the first term of the expansion, what is the resulting equation for Δ λ/λ? If instead, we assume that Figure a applies and that A), is due to a Doppler effect, then from Equation 37.36 we have Δ λ / λ = v / c, where v is the radial velocity of galaxy A relative to Earth.
(e) Using Hubble's law, compare this Doppler-effect result with the cosmological-expansion result of (d) and find a value for s. From this analysis you can see that the two results, derived with very different models about the redshift of the light we detect from distant galaxies, are compatible.
Suppose that the light we detect from galaxy A has a redshift of Δ λ / λ = 0.050 and that the expansion rate of the universe has been constant at the current value given in the chapter. (f) Using the result of (b), find the distance between the galaxy and Earth when the light was emitted. Next, determine how long ago the light was emitted by the galaxy
(g) by using the result of (a) and
(h) by assuming that the redshift is a Doppler effect the time is just the distance at the time of emission divided by the speed of light, because if the redshift is just a Doppler effect, the distance does not change during the light's travel to us. Here the two models about the redshift of the light differ in their results.)
(i) At the time of detection, what is the distance between Earth and galaxy A? (We make the assumption that galaxy, 4 still exist; if it ceased to exist, humans would not know about its death until the last light emitted by the galaxy reached Earth.) Now suppose that the light we detect from galaxy B (Figure c) has a redshift of Δ λ / λ = 0.080.
(j) Using the result of (b), find the distance between galaxy B and Earth when the light was emitted.
(k) Using the result of (a), find how long ago the light was emitted by galaxy B.
(l) When the light that we detect from galaxy A was emitted, what was the distance between galaxy A and galaxy B?
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals of Physics
ISBN: 978-0471758013
8th Extended edition
Authors: Jearl Walker, Halliday Resnick





