The combined resistance R of two resistances R 1 and R 2 connected in parallel [see Fig.
Question:
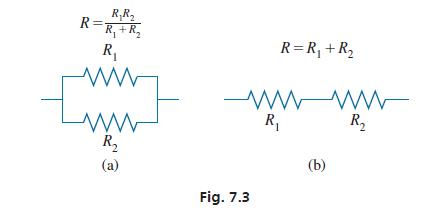
The combined resistance R of two resistances R1 and R2 connected in parallel [see Fig. 7.3(a)] is equal to the product of the individual resistances divided by their sum. If the two resistances are connected in series [see Fig. 7.3(b)], their combined resistance is the sum of their individual resistances. If two resistances connected in parallel have a combined resistance of 3.0 Ω and the same two resistances have a combined resistance of 16Ω when connected in series, what are the resistances?
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Basic Technical Mathematics
ISBN: 9780137529896
12th Edition
Authors: Allyn J. Washington, Richard Evans
Question Posted:





