The van der Waals equation for n moles of a gas is where P is the pressure,
Question:
The van der Waals equation for n moles of a gas is
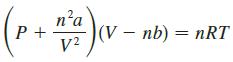
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, and T is the temperature of the gas. The constant R is the universal gas constant and a and b are positive constants that are characteristic of a particular gas.
(a) If T remains constant, use implicit differentiation to find dV/dP.
(b) Find the rate of change of volume with respect to pressure of 1 mole of carbon dioxide at a volume of V = 10 L and a pressure of P = 2.5 atm. Use a = 3.592 L2-atmymole2 and b = 0.04267 Lymole.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Calculus Early Transcendentals
ISBN: 9781337613927
9th Edition
Authors: James Stewart, Daniel K. Clegg, Saleem Watson, Lothar Redlin
Question Posted:





