DNA fragments introduced into an electrophoresis apparatus (see Application, page 360) generally carry negative charges equivalent to
Question:
DNA fragments introduced into an electrophoresis apparatus (see Application, page 360) generally carry negative charges equivalent to two extra electrons per base pair of nucleotide in the fragment. The table below shows the forces on several DNA fragments in an electroscopes apparatus, as a function of the number of base pairs. Plot these data, establish a best-fit line, and use the resulting slope to determine the strength of the electric field in the electroscopes apparatus.
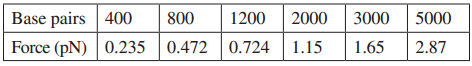
Data From Page 360
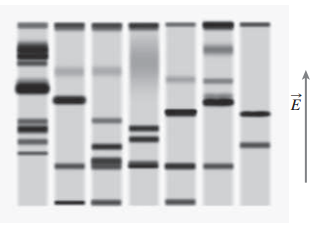
Electrophoresisis a widely used application of electric fields for separating molecules by size and molecular weight. It?s especially useful in ?biochemistry and molecular biology for distinguishing larger molecules like proteins and DNA fragments. In the commonly used gel electrophoresis, molecules carrying electric charge ?move through a semisolid but permeable gel under the influence of a uniform electric field; the greater the charge, the greater the electric force. The gel exerts a retarding force that increases ?with increasing molecular size, with the result that each molecular species moves at a velocity ?that depends on its size and charge. After a given time, the electric field is switched off. The lo-cations of the molecules then serve as indicators of their size, with the molecules that traveled ?farthest being the smallest. The photo shows a ?typical gel electrophoresis result. Here DNA fragments were introduced into the seven chan-nels at the top of the gel and then moved down-ward; their final locations indicate molecular size. The smaller molecules?those with fewer nucleotide base pairs?end up farther down on the gel. The electric field is shown by the arrow; it needs to point upward because DNA frag-ments carry a negative charge.
Step by Step Answer:






