A summary of the balance sheet of Travellers Inn Inc. (Til), a company that was formed by
Question:
A summary of the balance sheet of Travellers Inn Inc. (Til), a company that was formed by merging a number of regional motel chains and that hopes to rival Holiday Inn on the North American scene, is shown below:
Travellers Inn: December 31, 2015 (Millions of Dollars)
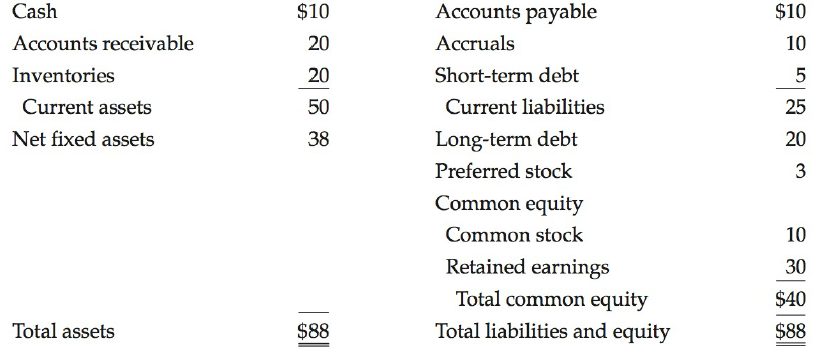
These facts are also given for Til:
(1) Short-term debt consists of bank loans that currently cost 10%, with interest payable quarterly. These loans are used to finance receivables and inventories on a seasonal basis, so in the off-season, bank loans are zero.
(2) The long-term debt consists of 20-year, semiannual payment mortgage bonds with a coupon rate of 8%. Currently, these bonds provide a yield to investors of rd = 7%. If new bonds were sold, they would yield investors 7%.
(3) Til's perpetual preferred stock has a $25 par value, pays a quarterly dividend of $0.45, and has a yield to investors of 6.5%. New perpetual preferreds would have to provide the same yield to investors, and the company would incur a 5% flotation cost to sell them.
(4) The company has 4 million shares of common stock outstanding. P0 = $20, but the stock has recently traded in the range of $17 to $23. 0 0 = $1 and EPS0 = $2. ROE based on average equity was 24% in 2015, but management expects to increase this return on equity to 30%; however, security analysts are not aware of management's optimism in this regard.
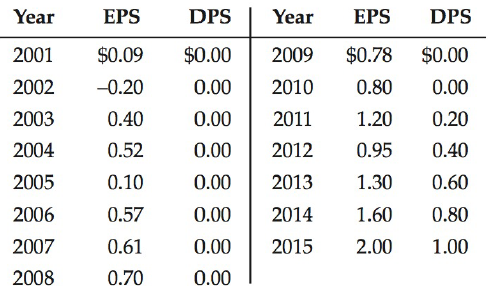
(5) Betas, as reported by security analysts, range from 1.3 to 1.7; the government bond rate is 5%; and RPM is estimated by various brokerage houses to be in the range of 2.5% to 3.5%. Brokerage house reports forecast growth rates in the range of 4% to 8% over the foreseeable future. However, some analysts do not explicitly forecast growth rates, but they indicate to their clients that they expect Til's historical trends, as shown in the table in fact (9), to continue.
(6) At a recent conference, Til's financial vice president polled some pension fund investment managers on the minimum rate of return they would have to expect on Til's common to make them willing to buy the common rather than Til bonds, when the bonds yielded 7%. The responses suggested a risk premium over Til bonds of 3 to 5 percentage points.
(7) Til is in the 30% tax bracket.
(8) Til's principal investment banker, Henry, Kaufman & Company, predicts a decline in interest rates, with rd falling to 6% and the government bond rate to 4%, although Henry, Kaufman & Company acknowledges that an increase in the expected inflation rate could lead to an increase rather than a decrease in rates.
(9) Here is the historical record of EPS and DPS:
Assume that you are a recently hired financial analyst and that your boss, the treasurer, has asked you to estimate the company's WACC; assume that no new equity will be issued. Your cost of capital should be appropriate for use in evaluating projects that are in the same risk class as the firm's average assets now on the books.
Balance SheetBalance sheet is a statement of the financial position of a business that list all the assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity and shareholder’s equity at a particular point of time. A balance sheet is also called as a “statement of financial... Cost Of Capital
Cost of capital refers to the opportunity cost of making a specific investment . Cost of capital (COC) is the rate of return that a firm must earn on its project investments to maintain its market value and attract funds. COC is the required rate of... Coupon
A coupon or coupon payment is the annual interest rate paid on a bond, expressed as a percentage of the face value and paid from issue date until maturity. Coupons are usually referred to in terms of the coupon rate (the sum of coupons paid in a... Dividend
A dividend is a distribution of a portion of company’s earnings, decided and managed by the company’s board of directors, and paid to the shareholders. Dividends are given on the shares. It is a token reward paid to the shareholders for their...
Step by Step Answer:

Financial Management Theory And Practice
ISBN: 978-0176583057
3rd Canadian Edition
Authors: Eugene Brigham, Michael Ehrhardt, Jerome Gessaroli, Richard Nason





