A firm is considering the replacement of a 2,000 lb capacity pressing machine purchased five years ago
Question:
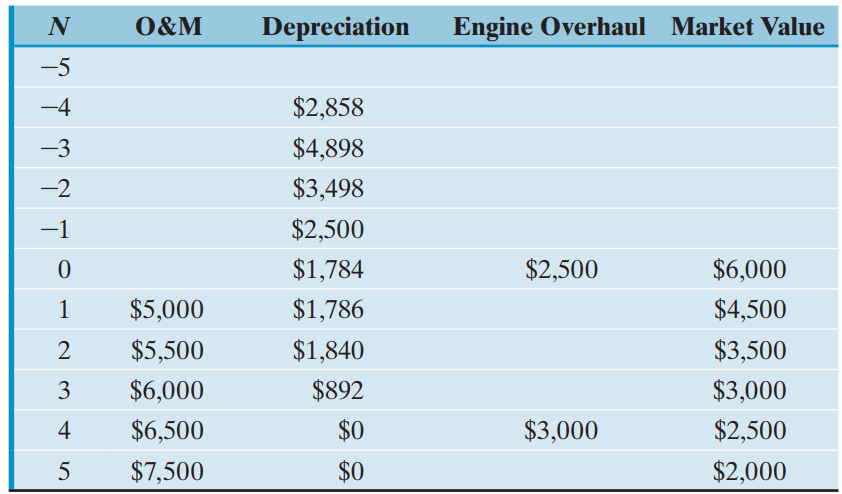
A drastic increase in operating costs during the fourth year is expected as a result of another overhaul, which will be required to keep the machine in operating condition. The firm€™s MARR is 15%.
(a) If the machine is to be sold now, what will be its sunk cost?
(b) What is the opportunity cost of not replacing the machine now?
(c) What is the equivalent annual cost of owning and operating the machine for two more years?
(d) What is the equivalent annual cost of owning and operating the machine for five more years?
Salvage value is the estimated book value of an asset after depreciation is complete, based on what a company expects to receive in exchange for the asset at the end of its useful life. As such, an asset’s estimated salvage value is an important... MARR
Minimum Acceptable Rate of Return (MARR), or hurdle rate is the minimum rate of return on a project a manager or company is willing to accept before starting a project, given its risk and the opportunity cost of forgoing other... Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost is the profit lost when one alternative is selected over another. The Opportunity Cost refers to the expected returns from the second best alternative use of resources that are foregone due to the scarcity of resources such as land,...
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





