Use the data given in CP13-1 for Golden Corporation. Required: 1. Compute the gross profit percentage for
Question:
Use the data given in CP13-1 for Golden Corporation.
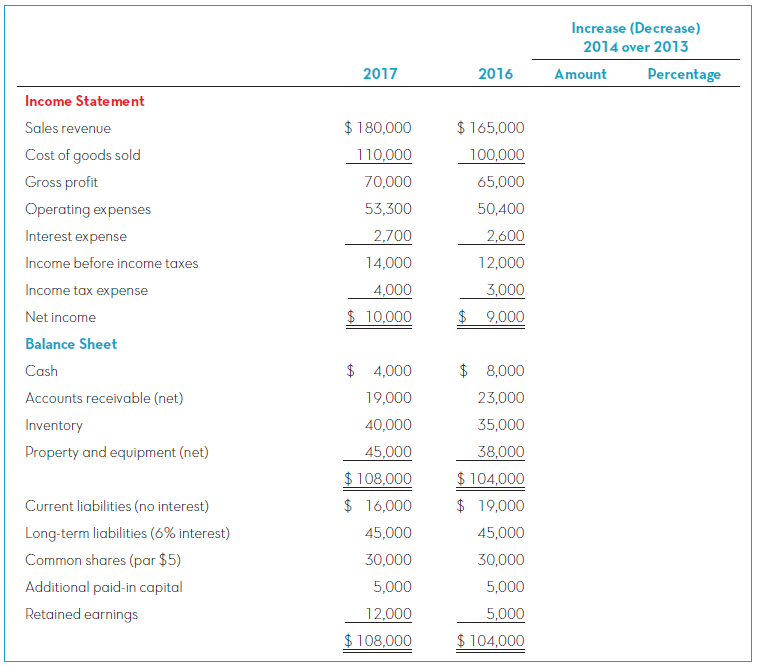
Required:
1. Compute the gross profit percentage for 2017 and 2016. Round the percentages to one decimal place. Is the trend going in the right direction?
2. Compute the net profit margin for 2017 and 2016. Round the percentages to one decimal place. Is the trend going in the right direction?
3. Compute the earnings per share for 2017 and 2016. Does the trend look good or bad? Explain.
TIP: To calculate EPS, use the balance in Common Shares to determine the number of shares outstanding. Common Shares equals the par value per share times the number of shares.
4. Shareholders? equity totalled $30,000 at the end of 2015. Compute the return on equity (ROE) ratios for 2016 and 2017. Express the ROE as percentages rounded to one decimal place. Is the trend going in the right direction?
5. Net property and equipment totalled $35,000 at the end of 2015. Compute the fixed asset turnover ratios for 2017 and 2016. Round the ratios to two decimal places. Is the trend going in the right direction?
6. Compute the debt-to-assets ratios for 2017 and 2016. Round the ratios to two decimal places. Is debt providing financing for a larger or smaller proportion of the company?s asset growth? Explain.
7. Compute the times interest earned ratios for 2017 and 2016. Round the ratios to one decimal place. Do they look good or bad? Explain.
8. After Golden released its 2017 financial statements, the company?s shares were trading at $30. After the release of its 2016 financial statements, the company?s share price was $21 per share. Compute the P/E ratios for both years, rounded to one decimal place. Does it appear that investors have become more (or less) optimistic about Golden?s future success?
Asset TurnoverAsset turnover is sales divided by total assets. Important for comparison over time and to other companies of the same industry. This is a standard business ratio. Par Value
Par value is the face value of a bond. Par value is important for a bond or fixed-income instrument because it determines its maturity value as well as the dollar value of coupon payments. The market price of a bond may be above or below par,...
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals of Financial Accounting
ISBN: 978-1259269868
5th Canadian edition
Authors: Fred Phillips, Robert Libby, Patricia Libby, Brandy Mackintosh





