A cross-flow molecular filtration device equipped with a mesoporous membrane is used to separate the enzyme lysozyme
Question:
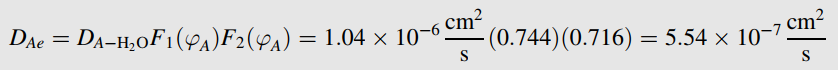
a. Show that the steady-state flux across the membrane and boundary layer is given by 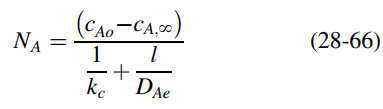
b. Estimate the average molar flux of the enzyme across the membrane and boundary layer, assuming the enzyme concentration at the bottom surface of the membrane (cAo) is maintained at 1.0 mmole/m3 and the bulk concentration of enzyme in the flowing liquid phase (cA,ˆž) is maintained at 0.40 mmole/m3. Also, estimate the flux for two limiting cases, one where convection mass-transfer limits the process, and another where molecular diffusion through the membrane limits the process.
c. What is the Biot number (Bi) for the enzyme mass-transfer process? Reflect on the importance of convective mass transfer.
d. How does the maximum thickness of the hydrodynamic boundary layer compare to the thickness of the membrane?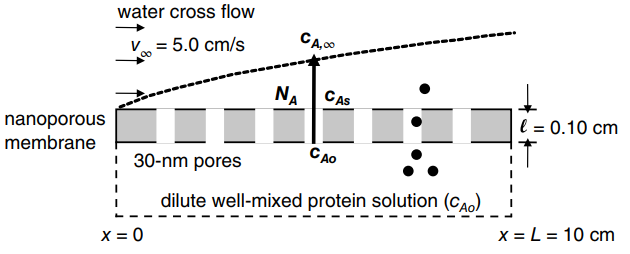
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals Of Momentum Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781118947463
6th Edition
Authors: James Welty, Gregory L. Rorrer, David G. Foster





