A stent is used to prop up a clogged artery to allow blood to pass through it.
Question:
a. What is the convective mass-transfer coefficient (kL) around the outer surface of the cylindrical portion of the stent, for the solute Taxol? State all assumptions.
b. What is the minimum time will it take for all of the Taxol to be completely discharged from the stent? State all assumptions.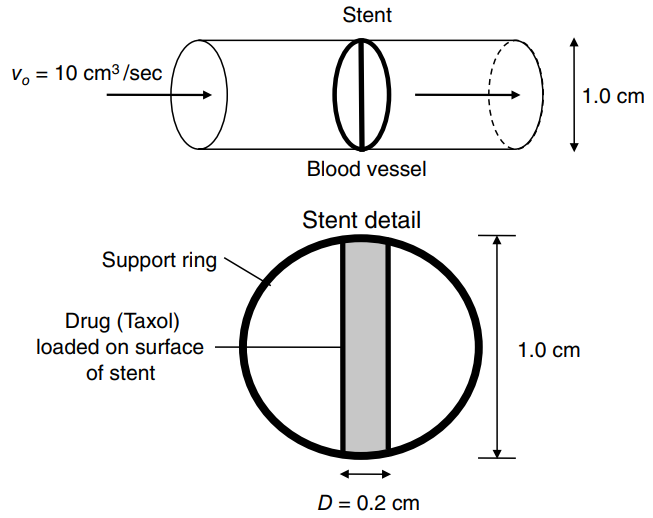
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Fundamentals Of Momentum Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781118947463
6th Edition
Authors: James Welty, Gregory L. Rorrer, David G. Foster
Question Posted:





