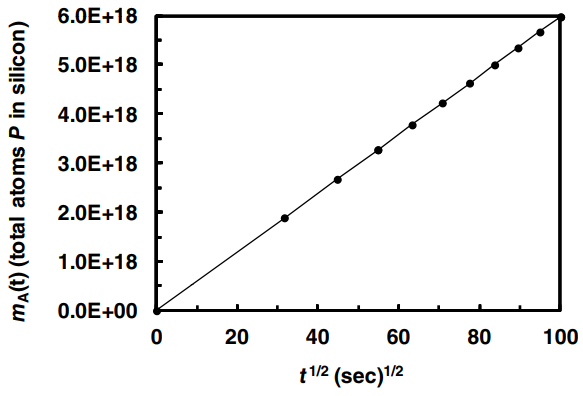
One step of the manufacturing of silicon solar cells is the molecular diffusion (doping) of elemental phosphorous
Question:
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Fundamentals Of Momentum Heat And Mass Transfer
ISBN: 9781118947463
6th Edition
Authors: James Welty, Gregory L. Rorrer, David G. Foster
Question Posted:





