Consider a country that can be divided into two distinct markets of different sizes: market 1 is
Question:
Consider a country that can be divided into two distinct markets of different sizes: market 1 is small (in the sense that it can only accommodate one firm), while market 2 is larger (in the sense that it can accommodate two firms). Two firms are active in the country: firm A is a national company that is active on both markets; firm B is a local company and is only active on market 2. Demand conditions on the two markets are as follows. On market 1 (where only firm A is active), inverse demand is given by qA1= a - pA1: On market 2 (where both firms are active and their products are seen as imperfect substitutes by the consumers), the system of inverse demands is
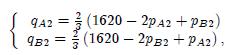
where qKi (resp. pKi) is the quantity demanded to (resp. the price set by) firm K in market i (K = A, B and i = 1, 2). To translate the fact that market 2 is larger than market 1, it is assumed that a < 1620. Both firms produce at a constant marginal cost, which is assumed to be equal to zero for simplicity.
1. Local pricing. Suppose that the national firm (firm A) chooses to adapt its prices to the local market conditions. Firm A has thus two choice variables: pA1 and pA2. As for the local firm (firm B), it has, by definition only one choice variable: pB2. Find the equilibrium prices of the two firms and then compute their equilibrium profits.
2. National pricing. Suppose now that firm A commits to set the same price in the two local markets. Denote this price by pA. As for firm B, nothing changes: it still sets its single price pB2. Find the equilibrium prices of the two firms and then compute their equilibrium profits.
3. Compare your answers to questions 1 and 2 by taking three specific values for the parameter a, namely a = 540, a = 1188, and a = 1260. In which scenario(s) does firm A prefer national pricing over local pricing? Explain the intuition behind your results. In which scenario(s) does firm B prefer that firm A sets the same price in the two markets (national pricing)? Explain the intuition behind your results.
Step by Step Answer:

Industrial Organization Markets and Strategies
ISBN: 978-1107069978
2nd edition
Authors: Paul Belleflamme, Martin Peitz





