On January 1, 2021, the general ledger of Tripley Company included the following account balances: The $30,000
Question:
On January 1, 2021, the general ledger of Tripley Company included the following account balances:
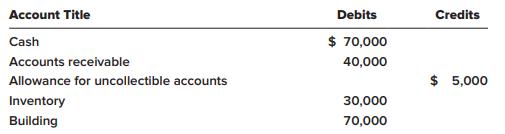
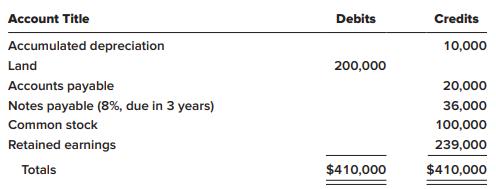
The $30,000 beginning balance of inventory consists of 300 units, each costing $100. During January 2021, the company had the following transactions:
Jan. 2 Lent $20,000 to an employee by accepting a 6% note due in six months.
5 Purchased 3,500 units of inventory on account for $385,000 ($110 each) with terms 1/10, n/30.
8 Returned 100 defective units of inventory purchased on January 5.
15 Sold 3,300 units of inventory on account for $429,000 ($130 each) with terms 2/10, n/30.
17 Customers returned 200 units sold on January 15. These units were initially purchased by the company on January 5. The units are placed in inventory to be sold in the future.
20 Received cash from customers on accounts receivable. This amount includes $36,000 from 2020 plus amount receivable on sale of 2,700 units sold on January 15.
21 Wrote off remaining accounts receivable from 2020.
24 Paid on accounts payable. The amount includes the amount owed at the beginning of the period plus the amount owed from purchase of 3,100 units on January 5.
28 Paid cash for salaries during January, $28,000.
29 Paid cash for utilities during January, $10,000.
30 Paid dividends, $3,000.
Required:
1. Record each of the transactions listed above in the ‘General Journal’ tab (these are shown as items 1-10) assuming a perpetual FIFO inventory system. Purchases and sales of inventory are recorded using the gross method for cash discounts. Review the ‘General Ledger’ and the ‘Trial Balance’ tabs to see the effect of the transactions on the account balances.
2. Record adjusting entries on January 31 in the ‘General Journal’ tab):
a. Of the remaining accounts receivable, the company estimates that 10% will not be collected.
b. Accrued interest revenue on notes receivable for January.
c. Accrued interest expense on notes payable for January.
d. Accrued income taxes at the end of January for $5,000. e. Depreciation on the building, $2,000
3. Review the adjusted ‘Trial Balance’ as of January 31, 2021, in the ‘Trial Balance’ tab.
4. Prepare a multiple-step income statement for the period ended January 31, 2021, in the ‘Income Statement’ tab.
5. Prepare a classified balance sheet as of January 31, 2021, in the ‘Balance Sheet’ tab.
6. Record closing entries in the ‘General Journal’ tab.
7. Using the information from the requirements above, complete the ‘Analysis’ tab.
a. Calculate the inventory turnover ratio for the month of January. If the industry average of the inventory turnover ratio for the month of January is 4.5 times, is the company selling its inventory more or less quickly than other companies in the same industry?
b. Calculate the gross profit ratio for the month of January. If the industry average gross profit ratio is 33%, is the company more or less profitable per dollar of sales than other companies in the same industry?
c. Used together, what might the inventory turnover ratio and gross profit ratio suggest about the company’s business strategy? Is the company’s strategy to sell a higher volume of less expensive items or does the company appear to be selling a lower volume of more expensive items?
Balance SheetBalance sheet is a statement of the financial position of a business that list all the assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity and shareholder’s equity at a particular point of time. A balance sheet is also called as a “statement of financial...
Step by Step Answer:

Intermediate Accounting
ISBN: 978-1260481952
10th edition
Authors: J. David Spiceland, James Sepe, Mark Nelson, Wayne Thomas





