Selected disclosures related to Foot Locker Company's inventory follow. Use these disclosures to answer the following questions:
Question:
Selected disclosures related to Foot Locker Company's inventory follow. Use these disclosures to answer the following questions:
a. What percentage of inventory at the end of 2016 is accounted for under each cost-flow assumption that Foot Locker uses?
b. Why would Foot Locker use LIFO for domestic U.S. inventories but FIFO for international inventories?
c. How does Foot Locker apply the retail inventory method?
d. What types of costs are included in the cost of sales?
e. Why does Foot Locker not report a LIFO reserve?
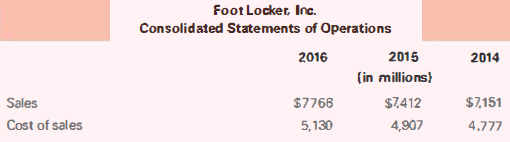
f. What is Foot Locker's gross profit percentage in 2014, 2015, and 2016?
g. What is Foot Locker's inventory turnover ratio and days inventory on hand in 2016?
NOTE 1: Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (excerpt)
Merchandise Inventories and Cost of Sales
Merchandise inventories for the Company's Athletic Stores are valued at the lower of cost or market using the retail inventory method. Cost for retail stores is determined on the last-in. first-out ("LIFO") basis for domestic inventories and on the first-in, first-out ("FIFO") basis tor international inventories. Merchandise inventories of the Direct-to-Customers business are valued at the lower of cost or market using weighted-average cost, which approximates FIFO.
The retail inventory method is commonly used by retail companies to value inventories at cost and calculate gross margins due to its practicality. Under the retail inventory method, cost is determined by applying a cost-to-retail percentage across groupings of similar items. known as departments. The cost-to-retail percentage is applied to ending inventory at its current owned retail valuation to determine the cost of ending inventory on a department basis. The Company provides reserves based on current selling prices when the inventory has not been marked down to market.
Transportation, distribution center, and sourcing costs are capitalized in merchandise inventories. The Company expenses the freight associated with transfers between its store locations in the period incurred. The Company maintains an accrual for shrinkage based on historical rates. Cost of sales is composed of the cost of merchandise, as well as occupancy, buyers' compensation, and shipping and handling costs. The cost of merchandise is recorded net of amounts received from suppliers for damaged product returns, markdown allowances, and volume rebates, as well as cooperative advertising reimbursements received in excess of specific, incremental advertising expenses. Occupancy includes the amortization of amounts received from landlords for tenant improvements.
NOTE 5: Merchandise Inventories

The value of the Company's LIFO inventories, as calculated on a LIFO basis, approximates their value as calculated on a FIFO basis.
Inventory Turnover RatioInventory Turnover RatioThe inventory turnover ratio is a ratio of cost of goods sold to its average inventory. It is measured in times with respect to the cost of goods sold in a year normally. Inventory Turnover Ratio FormulaWhere,... Ending Inventory
The ending inventory is the amount of inventory that a business is required to present on its balance sheet. It can be calculated using the ending inventory formula Ending Inventory Formula =... Distribution
The word "distribution" has several meanings in the financial world, most of them pertaining to the payment of assets from a fund, account, or individual security to an investor or beneficiary. Retirement account distributions are among the most...
Step by Step Answer:

Intermediate Accounting
ISBN: 978-0134730370
2nd edition
Authors: Elizabeth A. Gordon, Jana S. Raedy, Alexander J. Sannella





