The human -tropomyosin gene is alternatively spliced to produce different forms of -tropomyosin mRNA in different cell
Question:
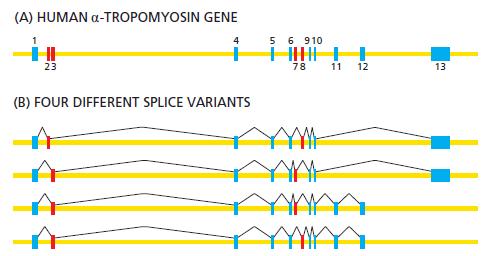
The human α-tropomyosin gene is alternatively spliced to produce different forms of α-tropomyosin mRNA in different cell types (Figure Q6–3). For all forms of the mRNA, the protein sequences encoded by exon 1 are the same, as are the protein sequences encoded by exon 10. Exons 2 and 3 are alternative exons used in different mRNAs, as are exons 7 and 8. Which of the following statements about exons 2 and 3 is the most accurate? Is that statement also the most accurate one for exons 7 and 8? Explain your answers.
A. Exons 2 and 3 must have the same number of nucleotides.
B. Exons 2 and 3 must each contain an integral number of codons (that is, the number of nucleotides divided by 3 must be an integer).
C. Exons 2 and 3 must each contain a number of nucleotides that when divided by 3 leaves the same remainder (that is, 0, 1, or 2).
Figure Q6-3
Step by Step Answer:

Molecular Biology Of The Cell
ISBN: 9780815344322
6th Edition
Authors: Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter





