Carbon disulfide, a key component in the manufacture of rayon fibers, is produced in the reaction between
Question:
Carbon disulfide, a key component in the manufacture of rayon fibers, is produced in the reaction between methane and sulfur vapor over a metal oxide catalyst:
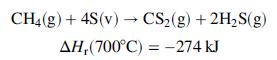
Methane and molten sulfur, each at 150°C, are fed to a heat exchanger in stoichiometric proportion. Heat is exchanged between the reactor feed and product streams, and the sulfur in the feed is vaporized. The gaseous methane and sulfur leave the exchanger and pass through a second preheater in which they are heated to 700°C, the temperature at which they enter the reactor. Heat is transferred from the reactor at a rate of 41.0 kJ/mol of feed. The reaction products emerge from the reactor at 800°C, pass through the heat exchanger, and emerge at 200°C with sulfur as a liquid. Use the following heat capacity data to perform the requested calculations: Cp[J/(mol ∙°C)] ≈ 29:4 for S(l), 36.4 for S(v), 71.4 for CH4(g), 31.8 for CS2(v), and 44.8 for H2S(g).
(a) Estimate the fractional conversion achieved in the reactor. In enthalpy calculations, take the feed and product species at 700°C as references.
(b) Suppose the heat of reaction at 700°C had not been given. What would be different in your solution to Part (a)? (Be thorough in your explanation.) Sketch the process paths from the feed to the products built into both the calculation of Part (a) and your alternative calculation. Explain why the result would be the same regardless of which method you used.
(c) Suggest a method to improve the energy economy of the process.
Step by Step Answer:

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes
ISBN: 978-1119498759
4th edition
Authors: Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard





