In Marcus theory for electron transfer, the reorganization energy is partitioned into solvent and solute contributions. Modeling
Question:
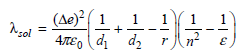
where Δe is the amount of charge transferred, d1 and d2 are the ionic diameters of ionic products, r is the separation distance of the reactants, n2 is the square of the index of refraction of the surrounding medium, and ε is the dielectric constant of the medium. In addition, (4πε 0)-1 = 8.99 × 109 J m C-2.
a. For an electron transfer in water (n = 1.33 and ε = 80.) for which the ionic diameters of both species are 6 Å and the separation distance is 15 Å, what is the expected solvent reorganization energy?
b. Redo the above calculation for the same reaction occurring in a protein. The dielectric constant of a protein is dependent on sequence, structure, and the amount of included water; however, a dielectric constant of 4 is generally assumed consistent with a hydrophobic environment.
Step by Step Answer:






