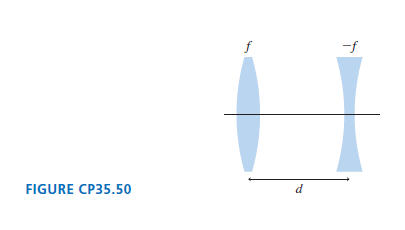
FIGURE CP35.50 shows a simple zoom lens in which the magnitudes of both focal lengths are f.
Question:
FIGURE CP35.50 shows a simple zoom lens in which the magnitudes of both focal lengths are f. If the spacing d < f, the image of the converging lens falls on the right side of the diverging lens. Our procedure of letting the image of the first lens act as the object of the second lens will continue to work in this case if we use a negative object distance for the second lens. This is called a virtual object. Consider an object very far to the left (s ?? ??) of the converging lens. Define the effective focal length as the distance from the midpoint between the lenses to the final image.
a. Show that the effective focal length is
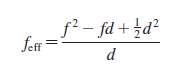
b. What is the zoom for a lens that can be adjusted from d = 1/2 f to d = 1/4 f?
-f FIGURE CP35.50 d
Step by Step Answer:
Visualize The effective focal length is defined as the distance from the midpoint between the two le...View the full answer



Physics for Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics
ISBN: 978-0133942651
4th edition
Authors: Randall D. Knight
Students also viewed these Physics questions
-
Zoom Lens Consider the simple model of the zoom lens shown in Fig. 34.43a The converging lens has focal length f1, = 12cm, and the diverging lens has focal length f1 = - 12cm. The lenses are...
-
Figure shows three forces applied to a trunk that moves leftward by 3.00 m over a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes ate F1 = 5.00N, F2 = 9.00N, and F3 = 3.00 N, and the indicated angle is ? =...
-
Two converging lenses having focal lengths of 10.0 cm and 20.0 cm are located 50.0 cm apart, as shown in Figure P36.74. The final image is to be located between the lenses at the position indicated....
-
At the beginning of the year, Plummer's Sports Center bought three used fitness machines from Advantage, Inc. The machines immediately were overhauled, installed, and started operating. The machines...
-
How does lifestyle relate to problem recognition?
-
The formaldehyde content of a pesticide preparation was determined by weighing 0.2985 g of the liquid sample into a flask containing 50.0 mL of 0.0959 M NaOH and 50 mL of 3% H2O2. Upon heating, the...
-
The case of flow past a cylinder of infinite length normal to the axis was also studied by Stokes. In view of the 2D nature of the problem, it is more convenient to work in \(r, \theta\) coordinates....
-
In the Vista City Hospital of Problem 8, Set 8.1a, suppose that only the bed limits represent flexible goals and that all the goals have equal weights. Can all the goals be met? Problem 8 Vista City...
-
Linux Construct a similar process tree on using pstree. You can store it in a file using redirection: pstree > hw3tree. Print it out and turn it in pdf form. Note that just using pstree may not be...
-
Estimate the common logarithm of 10 using-linear interpolation. (a) Interpolate between log 8 = 0.903900 and log 12 = 1.0791812. (b) Interpolate between log 9 = 0.9542425 and log 11 = 1.0413927. For...
-
The lens shown in FIGURE CP35.49 is called an achromatic doublet, meaning that it has no chromatic aberration. The left side is flat, and all other surfaces have radii of curvature R. a. For parallel...
-
FIGURE Q36.1 shows two balls. What are the speed and direction of each (a) In a reference frame that moves with ball 1. (b) In a reference frame that moves with ball 2? 6 m/s 3 m/s FIGURE Q36.1
-
Sketch the following planes in the window [0, 5] [0, 5] [0, 5]. The plane parallel to the xz-plane containing the point (1, 2, 3)
-
Georgia will be home to Hyundai's first dedicated EV plant and battery manufacturing facility in the United States, the company announced Friday. Hyundai is investing almost $5.5 billion to the EV...
-
Required Information [The following Information applies to the questions displayed below.] Laker Company reported the following January purchases and sales data for its only product. For specific...
-
When building a skill-based plan executive management is the source of information on defining the skills, arranging them into hierarchy, bundling them into skill blocks, and certifying whether a...
-
In Behn's (1995) article "The Big Questions of Public Management" he focuses on the three concepts of Micromanagement, Motivation and Measurement. However all three center around a central concept....
-
1)How many First Nations live around the Great Lakes Basin? 2)Who are the Anishinaabe? 3)Who are the Haudenosaunee? 4)How cultural diversity within the Indigenous population is frequently not...
-
Steve Szabo, a Venezuelan resident, had a checking account with the Bank of America in Palm Beach Gardens, Florida. Someone with an internet address in Nigeria hacked into Szabos accounts on-line,...
-
C- Consider the following scenario:- A supermarket needs to develop the following software to encourage regular customers. For this, the customer needs to supply his/her residence address, telephone...
-
Both nuclear and geothermal power plants use saturated steam in Rankine cycles. What are the fundamental differences between the thermodynamics of these two energy sources?
-
Assume that enthalpy is a linear function h(s, T) = as + bT. Consider a single-flash cycle, assuming that the saturated liquid and vapor curves between T ? and T +? form an isosceles trapezoid, i.e....
-
Determine the current relative costs of crude oil, gasoline, coal, and natural gas on a per unit of energy basis.
-
A bank can either invest money for three months at 4.00% or for nine months at 4.50%. Ignoring actual/360 day count adjustments for the purpose of this question, the three against nine FRA quote the...
-
Shuggy Otis, an executive at Slapfish Corp. (SC) intends to retire in 11 years. SC just announced that it will start depositing $500.00 at the end of each quarter into each of its workers' retirement...
-
On January 1, the Hanover Beverage Company replaced the palletizing machine on one of its juice lines. The cost of the machine was $195,000. The machine's expected life is five years or 480,000...

Study smarter with the SolutionInn App


