1. A beam of neutrons of constant velocity, mass M. (M. 1.67 x 10 * kg) and...
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Question:
1. A beam of neutrons of constant velocity, mass M. (M. 1.67 x 10 * kg) and energy E, is incident on a linear chain of atomic nuclei, arranged in a regular fashion as shown in the figure ........................................ 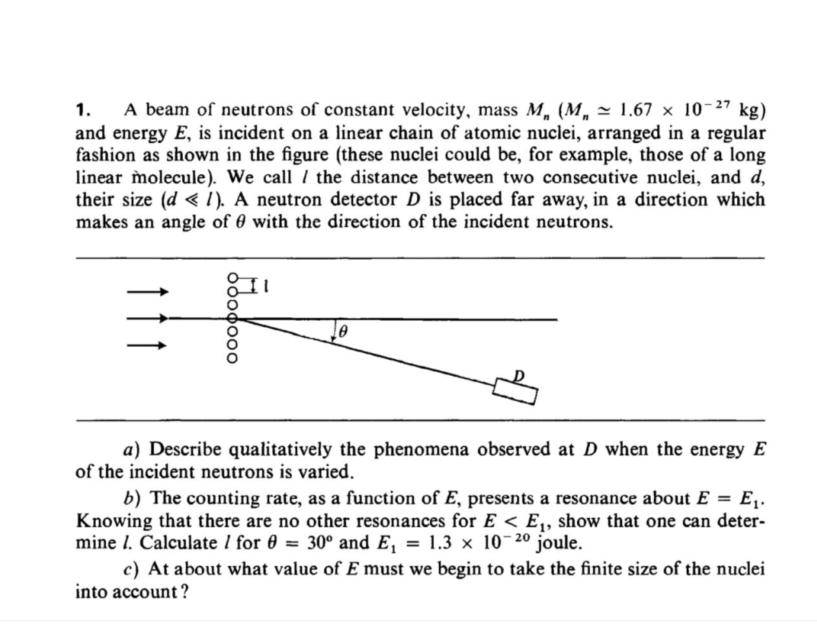
Transcribed Image Text:
1. A beam of neutrons of constant velocity, mass M, (M, 1.67 x 10-27 kg) and energy E, is incident on a linear chain of atomic nuclei, arranged in a regular fashion as shown in the figure (these nuclei could be, for example, those of a long linear molecule). We call / the distance between two consecutive nuclei, and d, their size (d < I). A neutron detector D is placed far away, in a direction which makes an angle of 6 with the direction of the incident neutrons. a) Describe qualitatively the phenomena observed at D when the energy E of the incident neutrons is varied. b) The counting rate, as a function of E, presents a resonance about E = E,. Knowing that there are no other resonances for E < E, show that one can deter- mine I. Calculate I for 6 30° and E, 1.3 x 10-20 joule. c) At about what value of E must we begin to take the finite size of the nuclei into account ? 0oo0000 1. A beam of neutrons of constant velocity, mass M, (M, 1.67 x 10-27 kg) and energy E, is incident on a linear chain of atomic nuclei, arranged in a regular fashion as shown in the figure (these nuclei could be, for example, those of a long linear molecule). We call / the distance between two consecutive nuclei, and d, their size (d < I). A neutron detector D is placed far away, in a direction which makes an angle of 6 with the direction of the incident neutrons. a) Describe qualitatively the phenomena observed at D when the energy E of the incident neutrons is varied. b) The counting rate, as a function of E, presents a resonance about E = E,. Knowing that there are no other resonances for E < E, show that one can deter- mine I. Calculate I for 6 30° and E, 1.3 x 10-20 joule. c) At about what value of E must we begin to take the finite size of the nuclei into account ? 0oo0000
Expert Answer:
Answer rating: 100% (QA)
In the experimental setup shown in the diagrama beam of nutrons is passing through a sequence of ato... View the full answer

Related Book For 

Physics
ISBN: 978-0077339685
2nd edition
Authors: Alan Giambattista, Betty Richardson, Robert Richardson
Posted Date:
Students also viewed these physics questions
-
A beam of neutrons is used to study molecular structure through a series of diffraction experiments. A beam of neutrons with a wide range of de Broglie wavelengths comes from the core of a nuclear...
-
A beam of neutrons has the same de Broglie wavelength as a beam of photons. Is it possible that the energy of each photon is equal to the kinetic energy of each neutron? If so, at what de Broglie...
-
A cast-steel C frame as shown in the figure has a rectangular cross section of 1.25 in by 2 in, with a 0.5-in-radius semicircular notch on both sides that forms midflank fluting as shown. Estimate A,...
-
Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Most Company has an opportunity to invest in one of two new projects. Project Y requires a $310,000...
-
Which ioh is the strongest nucleophile in aqueous solution? (a) F- (b) Cl- (c) Br- (d) I- (e) All of these are equally strong.
-
Reconsider the paper towel absorbency data from Exercise 10-13. Find a 95% confidence interval on the difference in the towels mean absorbency produced by the two processes. Assume the standard...
-
In 1940, the family of Thomas Back entered into an oil-and-gas lease with the Inland Gas Corporation. The lease held that Inland would pay to Backs family 12 cents per thousand cubic feet of gas...
-
Second Chance Welding rebuilds spot welders for manufacturers. The following budgeted cost data for 2014 is available for Second Chance. The company desires a $30 profit margin per hour of labor and...
-
Consider the two classes represented in the following UML diagram. Implement the two classes as explained below. YouTube Channel -owner: String -nbOfVideos: int -videos: Video[] +YouTubeChannel...
-
Convert 1250 millimeters to meters.
-
What is the present value of 100 shares of stock that will pay an annual dividend of $5 per share and will be sold in 8 years for $80 per share? Assume that the investor receives the last dividend on...
-
A sprinter set a high school record in track and field, running 2 0 0 . 0 m in 2 1 . 8 s . What is the average speed of the sprinter in kilometers per hour?
-
1. Create a JUnit test case to test the following method [2 points] public static int factorial(int n) { int fact = 1; } for (int i = 2; i
-
The following information is related to Best Breweries Inc. Total assets $11,000 Current assets $4,300 Contributed capital $3,500 Beginning retained earnings $1,700 Net sales $8,750 Net income $700...
-
(a) (fog)(x) (c) f(g(-2)) f(x) = 3x + 4, Find (b) (gof)(x) (d) g(f(3)) g(x) = 5x
-
You stand on a boat and notice waves coming towards you at a speed of 3.2 m/s. When they hit your boat, it takes you 1.8 s to go from the level of the flat sea to the highest point. Find the...
-
You want to host a giveaway on Facebook to promote your new side hustle. You are giving away a $50 gift card for your business. Anyone who likes/follows your Facebook page is entered into the...
-
Cassandra Casey operates the Futuristic Antique Store. She maintains subsidiary ledgers for accounts payable and accounts receivable. She presents you with the following information for October 2019:...
-
An American visitor to Finland is surprised to see heavy metal frames outside of all the apartment buildings. On Saturday morning the purpose of the frames becomes evident when several apartment...
-
The pulse of Problems 37-38 travels on a string that has fixed ends. 1. The pulse travels on a string whose ends at x = 0 and x = 4.0 m are both fixed in place. Sketch the shape of the string at t =...
-
The photosensitive cells (rods and cones) in the retina are most densely packed in the fovea-the part of the retina used to see straight ahead. In the fovea, the cells are all cones spaced about 1 m...
-
What are Incoterms? Give examples.
-
Distinguish between public international law and private international law.
-
What is meant by the proper law of the contract?

Study smarter with the SolutionInn App


