Production of paper requires a pulping step to break down wood chips into cellulose and lignin. In
Question:
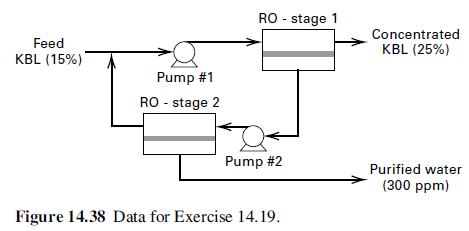
Production of paper requires a pulping step to break down wood chips into cellulose and lignin. In the Kraft process, an aqueous solution known as white liquor and consisting of dissolved inorganic chemicals such as Na2S and NaOH is used. Following removal of the pulp (primarily cellulose), a solution known as weak Kraft black liquor (KBL) is left, which is regenerated to recover white liquor for recycle. In this process, a 15 wt% (dissolved solids) KBL is concentrated to 45 to 70 wt % by multieffect evaporation. It has been suggested that reverse osmosis be used to perform an initial concentration to perhaps 25 wt%. Higher concentrations may not be feasible because of the high osmotic pressure, which at 180°F and 25 wt% solids is 1,700 psia. Osmotic pressure for other conditions can be scaled with (14-102) using wt% instead of molality. A two-stage RO process, shown in Figure 14.38, has been proposed to carry out this initial concentration for a feed rate of 1,000 lb/h at 180°F. A feed pressure of 1,756 psia is to be used for the first stage to yield a permeate of 0.4 wt% solids. The feed pressure to the second stage is 518 psia to produce water of 300 ppm dissolved solids and a retentate of 2.6 wt% solids. Permeate-side pressure for both stages is 15 psia. Equation (14-93) can be used to estimate membrane area, where the permeance for water can be taken as 0.0134 lb/ft2-hr-psi in conjunction with an arithmetic mean osmotic pressure for plug flow on the feed side. Complete the material balance for the process and estimate the required membrane areas for each stage. Reference: Gottschlich, D.E., and D.L. Roberts. Final Report DE91004710, SRI International, Menlo Park, CA, Sept. 28, 1990.

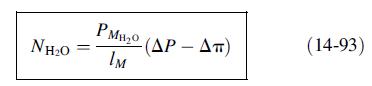
Step by Step Answer:

Separation Process Principles Chemical And Biochemical Principles
ISBN: 9780470481837
3rd Edition
Authors: By J. D. Seader, Ernest J. Henley, D. Keith Roper





