The mice in the study had body mass measured throughout the study. Computer output showing an analysis
Question:
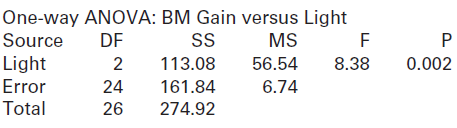
(a) State the null and alternative hypotheses.
(b) What is the F-statistic? What is the p-value? What is the conclusion of the test?
(c) Does there appear to be an association between the two variables (body mass gain and light condition)? If so, discuss the nature of that relationship. Under what light condition do mice appear to gain the most weight?
(d) Can we conclude that there is a cause-and-effect relationship between the variables? Why or why not?
Studies have shown that exposure to light at night is harmful to human health. Data A.1 on page 136 introduces a study in mice showing that even low-level light at night can interfere with normal eating and sleeping cycles and can have an effect on weight gain and glucose intolerance. In the study, mice were randomly assigned to live in one of three light conditions: LD had a standard light/dark cycle, LL had bright light all the time, and DM had dim light when there normally would have been darkness.
Data A.1 on page 136
Numerous studies have shown that exposure to light at night is harmful to human health. A recent study in mice shows that even low-level light at night can interfere with normal eating and sleeping cycles. Furthermore, the study finds that food is especially fattening if consumed at the wrong time of day, at least in mice. In the study, 27 mice were randomly split into three groups. One group was on a normal light€“dark cycle (LD), one group had bright light on all the time (LL), and one group had light during the day and dim light at night (DM). The dim light was equivalent to having a television set on in a room. The mice in darkness ate most of their food during their active (nighttime) period, matching the behavior of mice in the wild. The mice in both dim light and bright light, however, consumed more than half of their food during the well-lit rest period, when most mice are sleeping. Although the data collected show that the three groups of mice ate approximately the same amount of food and had the same levels of physical activity, the mice exposed to light at night gained substantially more weight, ate a greater percent of calories during the day, and were more likely to be classified as glucose intolerant at the end of the study. An absence of darkness seems to be associated with fatter mice.

Step by Step Answer:

Statistics Unlocking The Power Of Data
ISBN: 9780470601877
1st Edition
Authors: Robin H. Lock, Patti Frazer Lock, Kari Lock Morgan, Eric F. Lock, Dennis F. Lock





