The Howland Carpet Company has grown rapidly during the past 5 years. Recently, its commercial bank urged
Question:
The Howland Carpet Company has grown rapidly during the past 5 years. Recently, its commercial bank urged the company to consider increasing its permanent financing. Its bank loan under a line of credit has risen to $250,000, carrying an 8 percent interest rate. Howland has been 30 to 60 days late in paying trade creditors. Discussions with an investment banker have resulted in the decision to raise $500,000 at this time. Investment bankers have assured the firm that the following alternatives are feasible (flotation costs will be ignored):
- Alternative 1: Sell common stock at $8.
- Alternative 2: Sell convertible bonds at an 8 percent coupon convertible into 100 shares of common stock for each $1,000 bond (that is, the conversion price is $10 per share).
- Alternative 3: Sell debentures at an 8 percent coupon, each $1,000 bond carrying 100 warrants to buy common stock at $10. John L. Howland, the president, owns 80 percent of the common stock and wishes to maintain control of the company. One hundred thousand shares are outstanding. The following are extracts of Howland's latest financial statements:
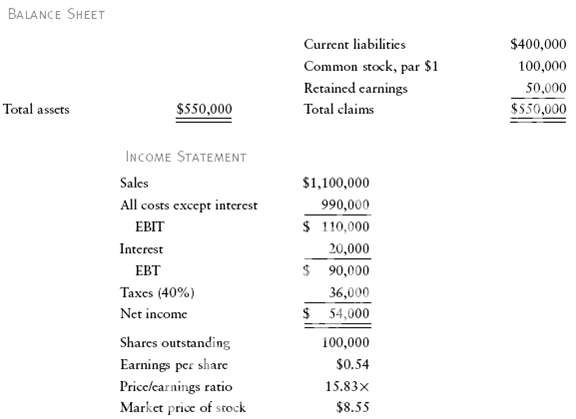
a. Show the new balance sheet under each alternative. For Alternatives 2 and 3, show the balance sheet after conversion of the bonds or exercise of the warrants. Assume that half of the funds raised will be used to pay off the bank loan and half to increase total assets.
b. Show Mr. Howland's control position under each alternative, assuming that he does not purchase additional shares.
c. What is the effect on earnings per share of each alternative, if it is assumed that profits before interest and taxes will be 20 percent of total assets?
d. What will be the debt ratio under each alternative?
e. Which of the three alternatives would you recommend to Howland, and why?
DebenturesDebenture DefinitionDebentures are corporate loan instruments secured against the promise by the issuer to pay interest and principal. The holder of the debenture is promised to be paid a periodic interest and principal at the term. Companies who... Common Stock
Common stock is an equity component that represents the worth of stock owned by the shareholders of the company. The common stock represents the par value of the shares outstanding at a balance sheet date. Public companies can trade their stocks on... Bonds
When companies need to raise money, issuing bonds is one way to do it. A bond functions as a loan between an investor and a corporation. The investor agrees to give the corporation a specific amount of money for a specific period of time in exchange... Balance Sheet
Balance sheet is a statement of the financial position of a business that list all the assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity and shareholder’s equity at a particular point of time. A balance sheet is also called as a “statement of financial... Coupon
A coupon or coupon payment is the annual interest rate paid on a bond, expressed as a percentage of the face value and paid from issue date until maturity. Coupons are usually referred to in terms of the coupon rate (the sum of coupons paid in a... Line of Credit
A line of credit (LOC) is a preset borrowing limit that can be used at any time. The borrower can take money out as needed until the limit is reached, and as money is repaid, it can be borrowed again in the case of an open line of credit. A LOC is...
Step by Step Answer:

Financial management theory and practice
ISBN: 978-0324422696
12th Edition
Authors: Eugene F. Brigham and Michael C. Ehrhardt





