Air is a source of reactants for many chemical processes, such as the synthesis of ammonia. To
Question:
Air is a source of reactants for many chemical processes, such as the synthesis of ammonia. To determine how much air is needed for these reactions, it is useful to know the partial pressures of the components. A certain sample of dry air of total mass 1.00 g consists almost entirely of 0.76 g of nitrogen and 0.24 g of oxygen. Calculate the partial pressures of these gases when the total pressure is 0.87 atm.
ANTICIPATE The molar masses of N2 and O2 are very similar, so very approximately you should expect the amounts of N2 and O2 to be in the ratio of the masses present, which is 0.76:0.24. The partial pressures should be in the same ratio, or about 3:1.
PLAN To use Eq. 4, the total pressure (given) and the mole fraction of each component are needed. The first step is to calculate the amount (in moles) of molecules of each gas present and the total amount (in moles). Then calculate the mole fractions from Eq. 2. To obtain the partial pressures of the gases, multiply the total pressure by the mole fractions of the gases in the mixture (Eq. 4)
What should you assume? There is no need to assume that the gases are ideal because Eqs. 4 and 1 are valid for any kind of gas.![]()
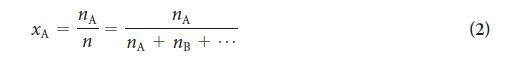
Step by Step Answer:

Chemical Principles The Quest For Insight
ISBN: 9781464183959
7th Edition
Authors: Peter Atkins, Loretta Jones, Leroy Laverman





