In an ionic crystal lattice each cation will be attracted by anions next to it and repulsed
Question:
In an ionic crystal lattice each cation will be attracted by anions next to it and repulsed by cations near it. Consequently the coulomb potential leading to the lattice energy depends on the type of crystal. To get the total lattice energy you must sum all of the electrostatic interactions on a given ion. The general form of the electrostatic potential is
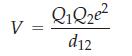
where Q1 and Q2 are the charges on ions 1 and 2, d12 is the distance between them in the crystal lattice. and e is the charge on the electron.
(a) Consider the linear “crystal” shown below.

The distance between the centers of adjacent spheres is R. Assume that the blue sphere and the green spheres are cations and that the red spheres are anions. Show that the total electrostatic energy is
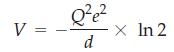
(b) In general, the electrostatic potential in a crystal can be written as
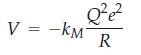
where kM is a geometric constant, called the Madelung constant, for a particular crystal system under consideration. Now consider the NaCl crystal structure and let R be the distance between the centers of sodium and chloride ions. Show that by considering three layers of nearest neighbors to a central chloride ion, kM is given by
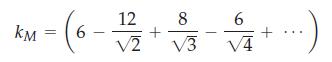
(c) Carry out the same calculation for the CsCl structure. Are the Madelung constants the same?
Step by Step Answer:

General Chemistry Principles And Modern Applications
ISBN: 9780132931281
11th Edition
Authors: Ralph Petrucci, Jeffry Madura, F. Herring, Carey Bissonnette





